
Older Adult Suicide Prevention: Tackling the Crisis Together
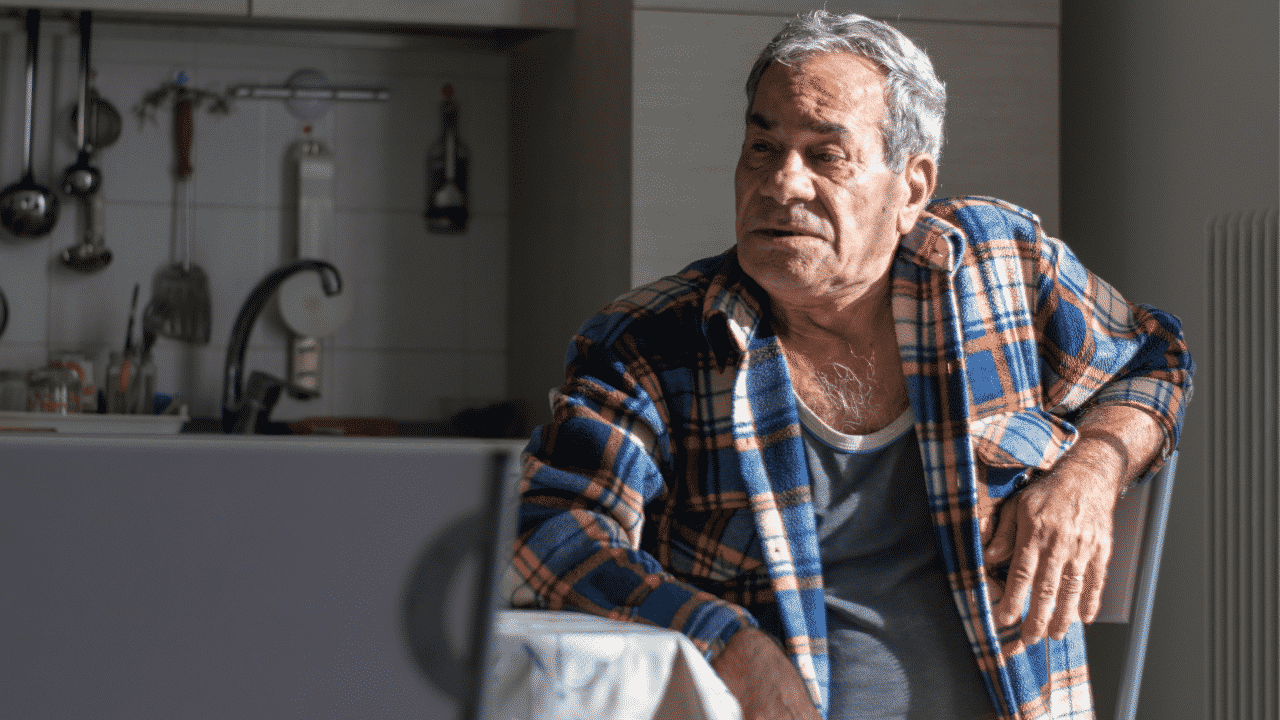
Older adult suicide prevention is a critical and increasingly urgent area of public health that demands our immediate attention. Recent studies reveal that adults aged 75 and older experience the highest suicide rates, often reflecting significant mental health challenges compounded by social isolation. Despite the escalating urgency, mental health resources for seniors remain insufficient, indicating a dire need for more accessible elderly suicide prevention resources. Organizations focused on geriatric psychiatry must prioritize creating tailored online suicide prevention initiatives specifically for this vulnerable population. By enhancing resources that target older adults, we can foster healthier communities and reduce the alarming trend of suicide among our seniors.
The topic of suicide prevention among older adults, often described as elderly suicide prevention, merits considerable focus as society grapples with rising suicide rates in this demographic. Mental health issues, compounded by factors like isolation and age-related stigma, necessitate comprehensive strategies to ensure that seniors receive the support they need. Many older adults are turning to digital platforms in their search for mental health resources, highlighting the importance of effective online suicide prevention campaigns that cater specifically to their experiences. Geriatric psychiatry plays a crucial role in addressing these issues and advocating for resources tailored to the unique challenges faced by this age group. It is essential to bridge the gap between growing mental health needs and the availability of proactive outreach and intervention strategies.
Understanding the High Suicide Rates Among Older Adults
Older adults represent a demographic with the highest suicide rates, particularly those aged 75 and older. This alarming statistic, reported at 20.3 per 100,000 by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), highlights an urgent public health crisis. Various factors contribute to this elevated risk, including increased social isolation, chronic physical health problems, and mental health issues that may remain underdiagnosed or untreated in this population. The CDC has noted a worrisome trend where the suicide rates in younger adults have been declining while the rates for older adults continue to ascend, indicating a dire need for targeted intervention strategies.
Research by organizations such as McLean Hospital emphasizes the need for tailored resources that cater specifically to older adults. Many seniors face barriers in accessing mental health services, including stigma and a lack of familiarity with available resources. This demographic may also express suicidal thoughts differently than younger individuals, leading to underreporting and misunderstanding of their plight. Thus, it is critical for mental health resources for seniors to be adaptable and relatable to their unique challenges.
The Gap in Online Suicide Prevention Resources for Seniors
Despite the increasing number of online resources for suicide prevention, many of these efforts do not effectively reach older adults. A recent study highlights that major organizations focused on suicide prevention often overlook the needs of this vulnerable population. While general mental health campaigns are prevalent, older adults are vastly underrepresented in these discussions, reflecting an imbalance in the accessibility of resources. It is paramount that these organizations recognize the distinct ways older adults search for health information, adapting their online presence to ensure that help is available and easily understandable.
Innovative strategies in online outreach are needed to bridge this gap. For instance, seniors frequently utilize familiar platforms such as Facebook or YouTube, where tailored messaging can resonate more with them. By incorporating geriatric psychiatry principles into these campaigns, there can be a greater focus on issues such as loneliness and social disconnect, which are pronounced in this age group. Online platforms must prioritize creating user-friendly environments where older adults can easily access crucial suicide prevention resources, thereby ensuring that help is merely a click away.
Community-Based Strategies for Elderly Suicide Prevention
Implementing community-based strategies can be pivotal in reducing suicide rates among older adults. Local initiatives that involve community centers and senior housing can foster environments of support and engagement, addressing the critical factors of social isolation that contribute to suicidal thoughts. Programs tailored for seniors can include peer support groups, regular mental health workshops, and community outreach to ensure that older adults feel more connected and less isolated in their daily lives. As relationships often falter as people age, fostering strong community ties can significantly influence mental health outcomes.
Additionally, partnerships with healthcare providers can enhance access to mental health services specifically designed for older individuals. Initiatives can focus on training healthcare professionals in geriatric mental health to better identify signs of distress in older adults. By increasing awareness and understanding of the issues older adults face, service providers can be better equipped to offer immediate support, ultimately leading to early intervention before crises arise. These comprehensive community strategies are vital for building resilience against factors leading to elderly suicide.
The Role of Geriatric Psychiatry in Suicide Prevention
Geriatric psychiatry plays a crucial role in understanding and preventing suicide among older adults. Professionals in this field are specifically trained to work with older populations, addressing their unique mental health needs. This specialization helps in the identification of risk factors often prevalent in older adults, such as cognitive decline, chronic illness, and the psychological impact of transitioning into retirement or losing loved ones. Their expertise is vital in developing effective prevention programs that are informed by the latest research and tailored to the distinct experiences of the elderly.
Moreover, geriatric psychiatrists can advocate for systemic changes in mental health services to ensure that resources are equitably distributed. Through research and clinical practice, they highlight the unique pathways older adults take when facing mental health challenges. Their involvement in developing policy initiatives can lead to improved mental health resources for seniors, ultimately fostering environments that prioritize the mental well-being of the aging population.
Utilizing Technology for Online Suicide Prevention
The intersection of technology and healthcare offers promising avenues for online suicide prevention, particularly among older adults. As more seniors become tech-savvy, leveraging platforms for mental health education and resource dissemination can significantly impact suicide rates. Creating user-friendly applications that provide mental health resources, emergency contact information, and easy access to trained professionals can empower older adults to seek help when needed. These technological advancements can also foster peer support networks, allowing seniors to share experiences and foster connections that alleviate feelings of loneliness.
Moreover, online suicide prevention interventions must consider the specific learning styles of older adults, ensuring that information is presented clearly and simply. Video tutorials, webinars, and interactive forums can provide engaging ways for seniors to understand and access mental health services. By utilizing technology to bridge the existing gaps in communication and resource availability, there is an opportunity to make significant strides in elderly suicide prevention efforts.
Expanding Mental Health Resources for Seniors
There is an urgent need to expand mental health resources for seniors, especially in light of the rising suicide rates among this age group. Efforts must focus on increasing funding for mental health initiatives that directly cater to older adults, including innovative outreach programs and accessible counseling services. By allocating resources towards developing educational materials that resonate with seniors, organizations can improve awareness of mental health issues and promote the importance of seeking help.
Partnerships between healthcare systems and community organizations can pave the way for comprehensive programs aimed at preventing elderly suicide. This collaboration can lead to the establishment of local helplines specialized in geriatric care, ensuring that older adults have direct access to support when they need it most. Furthermore, integrating mental health training within existing aging services can effectively enhance the quality of assistance provided to seniors, facilitating not just intervention but also ongoing support.
Addressing Social Isolation as a Risk Factor
Social isolation is a significant risk factor that exacerbates the likelihood of suicide among older adults. As individuals age, they may experience decreased mobility, lost connections with family and friends, or face the challenges of living alone. These conditions can lead to feelings of loneliness and despair, forcing the elderly into a vulnerable state of mind. Combating social isolation should be a cornerstone of any elderly suicide prevention strategy, as fostering connections can provide mental health benefits and improve overall quality of life.
Community programs aimed at encouraging social interaction—such as senior clubs, volunteer opportunities, and group outings—can effectively reduce the impact of isolation. Encouraging intergenerational activities and mentorship programs can also foster connections, allowing older adults to share their wisdom and life experience with younger generations. By creating inclusive environments that promote social engagement, communities can mitigate one of the most critical risk factors associated with elderly suicide.
The Importance of Tailored Suicide Prevention Programs
Tailored suicide prevention programs are essential in effectively reaching older adults. These initiatives must consider cognitive, emotional, and physical changes that can impact mental health. Programs should be designed with input from geriatric mental health professionals, seniors themselves, and their families to ensure they address specific needs. Additionally, involving older adults in the creation and implementation of these programs promotes a sense of ownership and acceptance, increasing the likelihood of participation and effectiveness.
Furthermore, continuous evaluation and adaptation of these programs are crucial in responding to the evolving landscape of mental health among older populations. As societal norms and technology change, so too must the methods used to engage with seniors about suicide prevention. By committing to personalized approaches, there is potential to develop sustainable strategies that make a significant impact in reducing suicide rates among older adults.
Raising Awareness About Elderly Suicide Prevention
Raising awareness about elderly suicide prevention is paramount in fostering community understanding and engagement regarding the issues facing older adults. Educational campaigns can empower people of all ages to recognize the signs of distress in seniors and provide them with the tools to offer support. Such campaigns can utilize various media platforms, including social media, public service announcements, and informational webinars, effectively reaching broader audiences and normalizing discussions around mental health.
Engaging community leaders, health organizations, and advocacy groups can amplify these efforts, creating a collective movement towards addressing the stigma associated with mental health in older adults. As knowledge spreads, communities can begin to dismantle the barriers preventing seniors from seeking help. Building an empathetic environment where discussions about mental health are welcomed will ultimately contribute to a reduction in suicide rates among elderly individuals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main factors contributing to high suicide rates among older adults?
Older adults, especially those aged 75 and older, face numerous risk factors for suicide, including social isolation, loneliness, and mental health challenges. These factors are often exacerbated by a lack of accessible mental health resources for seniors. Age-related changes and chronic health issues also contribute to feelings of hopelessness, making suicide prevention for this demographic crucial.
Why are mental health resources for seniors inadequate for suicide prevention?
Mental health resources for seniors are often insufficient due to their underrepresentation in research and limited outreach efforts from national suicide prevention organizations. Many online suicide prevention resources do not specifically target older adults, leading to an imbalance and unmet needs in this vulnerable population. Enhancing these resources can significantly benefit elderly suicide prevention.
How can geriatric psychiatry improve suicide prevention efforts for older adults?
Geriatric psychiatry plays a key role in addressing the unique mental health needs of older adults. By incorporating targeted interventions and developing specialized suicide prevention programs tailored to this age group, geriatric psychiatrists can better support at-risk individuals. Increased awareness and collaboration between healthcare professionals can also lead to improved access to necessary resources.
What online suicide prevention resources are available for older adults?
While there are various online suicide prevention resources, many are not easily accessible to older adults. However, organizations like the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline and the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration offer hotline services and online support. Efforts should focus on increasing the visibility of these resources to ensure older adults can access essential help when needed.
What types of elderly suicide prevention resources are needed?
Elderly suicide prevention resources should include accessible online platforms that provide information on mental health care, social support networks, and crisis intervention services tailored specifically for senior citizens. Additionally, campaigns focused on raising awareness of available services and promoting community engagement can significantly help reduce suicide rates among older adults.
How can families help prevent suicide in older adults?
Families can play a vital role in preventing suicide in older adults by maintaining open communication, recognizing warning signs of mental distress, and encouraging them to seek help. They should be aware of mental health resources for seniors and offer support in connecting with healthcare providers. Social interaction and emotional support can also alleviate feelings of loneliness, a significant risk factor for suicide.
What can be done to promote online suicide prevention targeted at older adults?
To promote online suicide prevention targeted at older adults, it is essential to create user-friendly websites and resources that reflect the specific needs of this age group. This includes simplifying language, incorporating large text, and avoiding technical jargon. Additionally, collaborating with geriatric specialists to ensure the delivery of crucial information can help engage this demographic more effectively.
What should individuals know about late-life suicide prevention?
Individuals should recognize that late-life suicide prevention requires a multifaceted approach, addressing mental health issues, social isolation, and access to care. Community support, awareness of mental health resources, and reducing stigma around seeking help are critical components. Awareness programs can aid in identifying at-risk individuals and ensuring they receive the proper support.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Highest Risk Group | Older adults aged 75 and older have the highest suicide rates. |
| Lack of Resources | National suicide prevention organizations do not provide adequate resources for older adults. |
| Study Findings | Research by McLean Hospital reveals an imbalance in online prevention efforts aimed at older adults. |
| Use of Online Resources | Older adults are increasingly using the internet to seek health information but find limited resources. |
| Targeted Campaigns Needed | There is a pressing need for campaigns specifically designed to address older adult suicide prevention. |
Summary
Older adult suicide prevention is a critical issue as this group faces significant risks that are often overlooked. The findings from recent studies underscore the urgent need for specialized resources and targeted campaigns to effectively address these challenges. By focusing on the unique healthcare needs and experiences of older adults, we can develop better strategies to reduce suicide rates and provide the necessary support for this vulnerable population. It is essential to raise awareness about the importance of older adult suicide prevention and ensure that effective resources are easily accessible online.
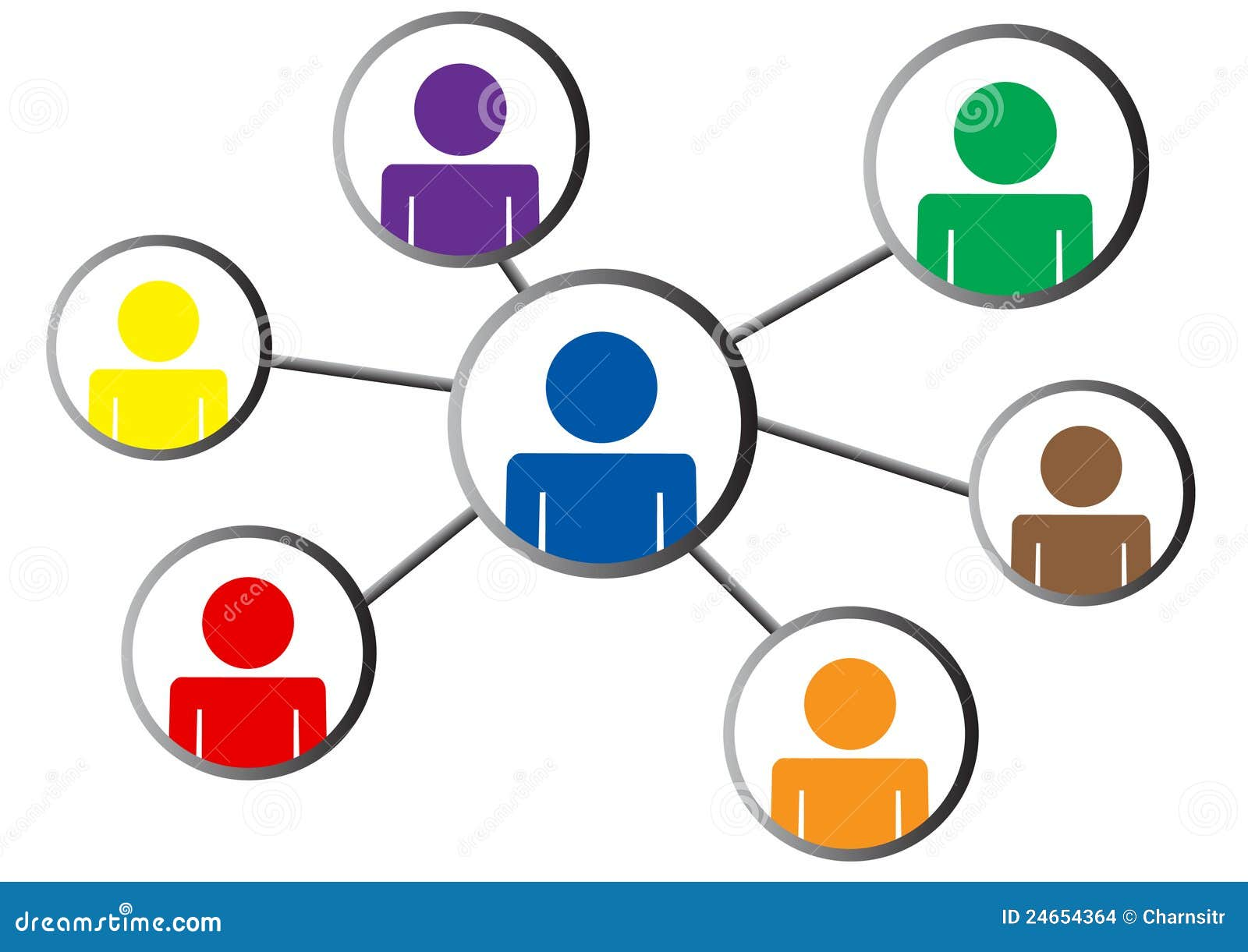
Social Connection: The Neurological Need for Interaction
In today’s fast-paced world, the importance of social connection has become increasingly evident as health professionals recognize it as a fundamental human need. Just as we need food, water, and shelter to thrive, our well-being is profoundly affected by our ability to engage in meaningful social interactions. Research indicates that social isolation can have detrimental effects on mental health, highlighting the crucial role social behavior plays in our lives. Understanding the neurological basis of loneliness helps illuminate why some individuals struggle with social needs and how these challenges can impact overall health. As we delve into the intersection of social connection and mental wellness, we uncover compelling insights that underscore the necessity of nurturing our relationships for a fulfilling life.
Recognizing the critical role of human interaction extends beyond merely social ties; it encompasses the entire spectrum of our social lives, which are essential for psychological health. Terms such as interpersonal relationships and community bonds illustrate the dynamic fabric of human engagement. Scientists and health experts alike are investigating how these connections influence our mental landscape and emotional well-being. The consequences of social withdrawal are being examined through a lens that connects physical and emotional health, reinforcing the view that our collective behavior shapes individual experiences. Harnessing research on social behavior can provide transformative insights into fostering healthier, more connected lives.
Understanding the Neurological Basis of Social Interaction
The growing recognition of social interaction as a fundamental human need parallels our understanding of physiological necessities like food and water. Research led by Ding Liu and his team at Harvard has begun to unearth the neurological basis for this essential aspect of our existence. By focusing on the hypothalamus, the brain region known to govern basic needs, scientists have identified specific neurons that are activated in response to social isolation. This groundbreaking work suggests that the desire for social connections may stem from a need to avoid negative emotions rather than purely from the pursuit of joy. The intricate dance of neurotransmitters like dopamine and oxytocin during these interactions underscores how deeply wired social behaviors are in our biology, altering our mental health landscape significantly as a result of social deprivation or connection.
Furthermore, understanding how the brain encodes the need for social interaction opens up new avenues for addressing mental health issues. The stark observations from mouse studies demonstrate that prolonged isolation diminishes the desire for social behavior. This has critical implications for humans, particularly in our increasingly digital and often isolating world. The decreasing interactions can exacerbate conditions such as depression and anxiety while reinforcing the importance of social bonds in maintaining mental well-being. By delving into the neurological foundations of social behavior, we begin to piece together a much larger puzzle that incorporates the mechanisms of loneliness and the social networks essential for a thriving life.
The Effects of Social Isolation on Mental Health
Social isolation is not merely a state of being alone; it has profound effects on mental health, leading to loneliness and heightened psychological distress. The observations from Liu’s research indicate that, when subjected to extended periods of isolation, even social creatures like mice begin to reject social interactions, leading to a troubling cycle of loneliness. This pattern is alarmingly similar in humans, where long-term isolation can manifest in mental health conditions like depression and anxiety disorder. The lack of regular, meaningful interactions can silence the brain’s natural desire for companionship, contributing to a deterioration in psychological health.
Studies have shown that mental health is intricately linked with the quality and quantity of social interactions. The importance of social interaction as a buffer against mental health decline cannot be overstated. The growing evidence suggests that having a robust social network can mitigate the adverse effects of stress, increase resilience to mental health issues, and enhance overall psychological well-being. By encouraging regular social contact, we can foster a healthier society and create strategies to combat the mentally debilitating effects of isolation.
Exploring the Impact of Touch on Social Needs
Touch plays a pivotal role in fulfilling social needs, serving as a crucial form of communication between individuals. The research conducted by Liu’s team indicates that not only visual and auditory cues but also tactile interactions are essential for maintaining social connections. Experiments with mice revealed a clear preference for environments that provided soft texture and tactile comfort, highlighting how touch can enhance feelings of safety and companionship. In human contexts, the significance of touch is equally vital. Whether it’s a comforting hug or a handshake, physical touch fosters emotional closeness and reinforces social bonds, underscoring the depth of our need for physical interactions.
In today’s fast-paced digital world, however, many individuals are starved of touch-based interactions, leading to a gradual estrangement from one another. This phenomenon has raised concerns among health professionals, particularly as remote communication often lacks tactile feedback. Research indicates that insufficient physical touch can contribute to feelings of loneliness and isolation, making it necessary to rethink how we build social connections in our increasingly screen-oriented lives. By recognizing and prioritizing the crucial role of touch in our social lives, we can strive to create environments that nurture our innate need for connection and camaraderie.
The Social Connection: A Human Rights Perspective
Recognizing social connection as an inherent human right has gained traction in recent years, especially considering its profound implications for mental health. In an era where social isolation has reached epidemic proportions, particularly following global events like the pandemic, understanding the importance of social ties is more urgent than ever. The U.S. Surgeon General’s recent emphasis on social connection highlights a growing consensus that the ability to forge relationships is not just beneficial but necessary for our overall well-being. Ensuring that individuals have opportunities for meaningful social contact upholds not only their mental health but also their humanity.
On a broader scale, advocating for social connection as a right compels us to examine systemic barriers that hinder interpersonal relationships. Issues such as economic disparity, lack of accessible spaces for gathering, or societal stigma against mental health create environments where isolation can flourish. Moving forward, it’s imperative for policymakers, mental health advocates, and communities to work collaboratively to dismantle these barriers. By fostering settings that encourage community engagement and connection, we can better prevent the detrimental effects of social isolation and strengthen the mental health framework essential for fostering a healthy, supportive society.
Research on Social Behavior: Key Findings and Implications
Research on social behavior has unveiled crucial insights into the mental health risks associated with social isolation. Studies show that social connections significantly buffer against the adverse effects of stress, while findings from Liu’s research suggest that the underlying neurological mechanisms for longing and isolation can be intricately linked. For instance, neurons activated during isolation reflect an instinctual drive to seek connection, confirming that our social needs are hardwired into our biology. These insights underline the importance of recognizing and enhancing social interaction as an essential component of mental health strategies.
Moreover, the implications of this research reach beyond individual mental health; they also touch upon collective societal norms. Encouraging research in this field could lead to more comprehensive mental health initiatives that integrate social behaviors into treatment plans, showing a monumental shift from merely treating symptoms to addressing root causes that stem from social disconnection. As we develop a better understanding of the multifaceted nature of social needs, we can tailor interventions that foster healthier relationships and community bonds, ensuring that mental health care is holistic, inclusive, and grounded in the realities of human connection.
Loneliness in the Modern Age: Challenges and Solutions
Loneliness has emerged as a significant public health crisis in the modern age, exacerbated by factors such as technology-driven communication, social media interactions, and urban disintegration. As noted by healthcare professionals, social isolation and loneliness are increasingly recognized not only as state-induced feelings but as real threats to physical and mental health. By exploring the roots of loneliness through scientific research, we can develop more effective approaches to combat this pervasive issue in society. Liu’s research on the neurological basis for social longing provides a framework for understanding why humans are wired to connect and the dire consequences of failing to do so.
To address the challenges posed by rampant loneliness, multifaceted solutions are required. Public health campaigns must aim to normalize the conversation around loneliness, encouraging individuals to seek social engagement actively. Community initiatives fostering inclusive spaces where people can connect, share experiences, and build relationships will be essential. In a society where face-to-face interactions are increasingly rare, re-establishing avenues for socializing is crucial. Whether it’s through shared activities, mental health support groups, or skill-building workshops, creating opportunities for authentic social engagement can counteract loneliness and promote holistic well-being.
Creating Support Systems for Mental Health and Social Needs
In light of the complexities surrounding social needs and mental health, building robust support systems is integral to ensuring emotional well-being within communities. Healthy support systems should encompass family, friends, and communities while promoting environments that encourage regular social interactions. As studies highlight the importance of companionship in maintaining mental health, developing accessible mental health resources in community centers can help provide critical support to those feeling isolated. Establishing networks that connect vulnerable individuals with peers or mentors can serve to bridge the gap of loneliness.
Moreover, engaging educational institutions in creating forums for social learning can enhance the importance of connection among young people. Crafting platforms that prioritize social skills can effectively nurture empathetic behaviors and awareness about mental health. Emphasizing cooperation through collaborative learning experiences can help instill a sense of community from an early age, reinforcing the idea that social connection is essential for a happy and healthy life. Such initiatives not only improve individual emotional well-being but also foster a harmonious social environment that values the intricate relationship between mental health and social bonds.
The Long-term Effects of Isolation on Health
The long-term effects of social isolation extend far beyond the immediate emotional responses; they can translate into significant health disparities as well. Research indicates that individuals who experience chronic social isolation face increased risks for a range of health issues including cardiovascular diseases, weakened immune function, and cognitive decline. These alarming findings support the assertion that social connections are not merely desirable but essential for physical health. Understanding the breadth of these implications calls for a more comprehensive approach to health that integrates social dynamics into routine care.
Furthermore, recognizing the extensive impact of social isolation on health underscores the need for targeted interventions aimed at re-establishing social networks. Initiatives aiming to reduce isolation should focus on vulnerable populations such as the elderly, who often suffer from a lack of engagement and companionship. By promoting social activities, meal programs, and community gatherings, we can foster relationships that mitigate the adverse effects of isolation and promote overall health. The value of social interaction as a protective measure underscores the critical role of community in healing and health maintenance.
Strategies for Enhancing Social Connections
Strategies for enhancing social connections are imperative as we confront the modern challenges of isolation. Organizations, both public and private, must prioritize social programming that facilitates genuine interactions among individuals. This could involve hosting community events, creating support groups, or leveraging technology to foster meaningful connections. Engaging individuals in collaborative tasks or activities can strengthen bonds and create a sense of belonging vital for mental health. Such initiatives not only empower individuals to build relationships but also invigorate community spirit.
Moreover, encouraging individuals to actively participate in their surroundings helps foster a culture of connection. Simple initiatives, such as neighborhood organizing, volunteering, or even joining clubs that align with personal interests create avenues for social interaction. These activities enhance life satisfaction and provide the social support necessary to combat isolation. By investing in our communities and nurturing relationships, we can build a resilient society that prioritizes the mental health of its members, fostering deep-rooted connections that stand the test of time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the importance of social interaction for mental health?
The importance of social interaction for mental health cannot be overstated. Research shows that meaningful social connections are essential for emotional well-being, akin to basic needs like food and water. Individuals lacking social interactions are at higher risk for mental health issues such as depression and anxiety. By fostering strong social ties, we enhance our resilience against stress and improve overall mental health.
How does social isolation affect our neurological health?
Social isolation has significant effects on neurological health, as recent studies indicate that the brain processes social needs similarly to physical needs, like hunger and thirst. Chronic isolation can lead to negative neurological impacts, diminishing the desire for social interaction and potentially contributing to mental illness. Understanding the neurological basis of loneliness helps us address these health issues more effectively.
What is the neurological basis of loneliness?
The neurological basis of loneliness involves specific brain circuits that regulate the urge for social connection. Neuroscientific research shows that areas in the hypothalamus activate during social deprivation, akin to how hunger is triggered by food scarcity. This suggests that loneliness is not only a psychological state but also a biological imperative, emphasizing the fundamental need for social connection in human life.
What are the effects of social isolation on behavior?
The effects of social isolation can include reduced motivation for social interaction, anxiety, and depression. Scientific studies have demonstrated that prolonged isolation can reshape social behavior by normalizing a lack of social engagement. Understanding these effects is crucial for developing interventions that encourage social connection and improve mental health outcomes.
How do social connections influence our overall well-being?
Social connections play a vital role in our overall well-being by providing emotional support, enhancing life satisfaction, and reducing feelings of loneliness. Engaging in robust social interactions activates brain pathways that promote happiness and can even combat the effects of stress. By prioritizing social relationships, we nurture our mental health and foster resilience.
What research exists on social behavior and mental health needs?
Research on social behavior underscores the intricate link between social connection and mental health. Studies reveal that individuals with strong social ties are less likely to experience mental health issues. The neurological studies, like those investigating the hypothalamic circuits involved in social interaction, highlight the biological underpinnings of our need for companionship, reinforcing its importance for mental health.
Why are meaningful social interactions considered as essential as food and water?
Meaningful social interactions are deemed as essential as food and water because they fulfill fundamental human psychological needs. Research indicates that social relationships influence physiological responses and brain functions, akin to the body’s reaction to hunger. Engaging with others helps maintain emotional balance and promotes health, making social connection a crucial aspect of holistic well-being.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Social Connection as a Basic Need | Health professionals recognize social connection as fundamental, similar to food and shelter. |
| Public Health Concern | The U.S. Surgeon General highlighted social isolation as a major public health issue in 2023. |
| Neurological Study | Research investigates how the brain encodes the desire for social connection. |
| The Role of the Hypothalamus | Study focuses on neural activity in the hypothalamus, which regulates basic needs like hunger and thirst. |
| Impact of Isolation | Prolonged isolation can diminish the desire for social interaction, complicating social needs. |
| Touch and Social Interaction | Touch is essential for social behavior, with implications for human interaction, especially in the digital age. |
Summary
Social connection plays a vital role in human health and well-being. Understanding its neurological basis, especially how it is intertwined with physiological needs like hunger and thirst, is crucial for addressing modern health challenges. This research underscores the importance of maintaining social interactions in our increasingly isolated and digital world, emphasizing that fostering social connections is essential for a healthier society.

How Much Sleep Do You Need? Discover Your Ideal Duration
How much sleep do you need? This vital question is essential for achieving optimal sleep health and sustaining overall well-being. The answer fluctuates for each individual, typically determined by how much sleep one gets naturally without interruptions from alarms or other obligations. Understanding the right sleep duration can significantly improve sleep quality, reducing the risk of insomnia and its associated challenges. In this exploration, we will delve into various sleep tips and insights to ensure you not only achieve the quantity of sleep required but also enhance its restorative quality.
Determining your optimal rest period is crucial for maintaining your health and vitality. The duration of sleep needed can vary widely depending on personal lifestyle and biological factors. Getting adequate sleep not only contributes to your well-being but also enhances your cognitive function and emotional stability. There are effective solutions to insomnia and sleep disturbances that can help tailor your night’s rest to suit your specific needs. By exploring relevant approaches and practices, you can improve your sleep routine and achieve a more rejuvenating slumber.
Understanding Sleep Duration: How Much Sleep Do You Need?
Sleep duration varies significantly from person to person, influenced by various factors such as age, lifestyle, and overall health. Understanding how much sleep you truly need can be daunting, especially when conflicting advice is abundant. A good rule of thumb is to observe how much sleep you naturally get when not disturbed by alarms or responsibilities. Keeping track of your sleep for several days can provide valuable insights into your sleep patterns, highlighting what feels restorative for you.
Sleep experts often suggest that most adults need between 7 to 9 hours of sleep per night, but this isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. If you consistently wake up feeling tired or groggy even after a full night’s sleep, it may indicate a deeper issue, such as insomnia or sleep disturbances. Prioritizing your sleep health is essential, and recognizing your individual sleep needs can transform your overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much sleep do you need for optimal health?
The amount of sleep you need varies by individual, but generally, adults should aim for 7-9 hours per night for optimal sleep health. Pay attention to how you feel after several nights of uninterrupted sleep to determine your personal sleep duration requirements.
What are some tips for achieving the sleep duration you need?
To achieve the sleep duration you need, establish a consistent sleep schedule, create a calming bedtime routine, and limit screen time before bed. Consider relaxation techniques like reading or using white noise to improve your sleep quality.
How does sleep quality affect how much sleep you need?
Sleep quality is crucial; if you experience poor sleep quality, you may require more sleep duration to feel rested. Factors like stress, noise, and environment significantly impact sleep quality, so it’s essential to create a conducive sleeping environment.
What to do if you’re not meeting your sleep duration needs?
If you’re struggling to meet your sleep duration needs, assess your lifestyle for potential disruptors, such as caffeine intake and screen time. Implementing sleep tips like practicing relaxation techniques before bedtime can also help you achieve better sleep.
How can you tell if you need to consult a doctor about your sleep?
If you consistently wake up feeling unrested, despite aiming for adequate sleep duration, or if you experience symptoms like snoring, insomnia, or waking frequently during the night, it’s advisable to consult a sleep doctor for potential sleep health issues.
What role does age play in determining how much sleep you need?
Age significantly influences sleep needs; children and teenagers typically require more sleep than adults, while older adults may experience changes in sleep patterns. Knowing your age-related sleep requirements can help you optimize your sleep duration.
Are there specific strategies for improving sleep health?
Improving sleep health involves maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a peaceful sleep environment, and managing stress. Additionally, avoiding stimulants before bedtime can enhance sleep quality and help achieve the sleep duration you need.
What is the relationship between sleep duration and insomnia solutions?
Chronic insomnia can disrupt your sleep duration, making it essential to explore effective insomnia solutions. Techniques such as cognitive behavioral therapy or lifestyle changes are proven to improve both sleep duration and quality.
How can melatonin affect sleep and your sleep duration needs?
Melatonin can help regulate sleep cycles and improve your sleep duration needs, especially when used appropriately. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for proper guidance on its use, as it is not regulated by the FDA.
How can relaxation techniques impact sleep quality and duration?
Incorporating relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga into your nightly routine can significantly enhance your sleep quality. Better sleep quality enables you to feel more rested, potentially reducing the overall sleep duration you may think you need.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Individual Sleep Needs | Sleep requirements vary by person; it’s best determined by how much sleep you get when not woken by an alarm. |
| Feeling Rested | If you continually wake up feeling unrefreshed after adequate sleep, a sleep specialist may be needed. |
| Sleep Disorders | Conditions like narcolepsy, sleep apnea, and insomnia can affect sleep quality and require medical attention. |
| Sleep Hygiene Tips | Establishing a calming pre-sleep routine and avoiding stimulants before bed can improve sleep quality. |
| Medication and Supplements | Melatonin is not FDA regulated. Long-term insomnia treatment is best approached with cognitive behavioral therapy. |
| Sleep Aids | Sound machines, earplugs, and eye masks may help with sleep, as long as they’re safe. |
Summary
How much sleep do you need can vary significantly from person to person. On average, adults typically require between 7-9 hours of sleep each night. However, factors like age, lifestyle, stress levels, and individual health play critical roles in determining one’s sleep needs. It’s essential to listen to your body and recognize when you feel rested versus when you’re experiencing sleep disturbances. Establishing a consistent bedtime routine and managing your sleep environment can help improve your sleep quality. If you find that you’re not feeling rested despite adequate sleep, consulting with a sleep specialist may be necessary to address underlying issues.

Heart Disease Prevention: Why We Must Take Action Now
Heart disease prevention is an essential topic that deserves our urgent attention, especially considering that cardiovascular disease remains the leading cause of death in America. With the alarming cardiovascular disease statistics showing that this condition kills more individuals than any form of cancer combined, understanding how to prevent heart disease is crucial. By engaging in cholesterol awareness and adopting effective cardiovascular health tips, individuals can significantly reduce their risk. One way to enhance prevention efforts is through proactive measures like the use of statins for cholesterol management, especially among those who might not yet view it as a serious concern. The message is clear: it’s time to shift our mindset and approach heart disease with the urgency it requires.
Preventing heart-related illnesses is increasingly recognized as a vital focus for maintaining overall health and well-being. As we navigate the complexities of cardiovascular health, many crucial aspects come into play, particularly the cumulative effects of lifestyle choices on our heart’s condition. With a growing emphasis on understanding personal health metrics, including managing cholesterol levels and hypertension, individuals are encouraged to be proactive. Initiatives designed to promote awareness about cardiovascular health can significantly impact individuals’ lives, reducing the likelihood of serious health issues down the line. This need for urgency in prevention strategies not only highlights a critical area of healthcare but also empowers individuals to take charge of their heart health proactively.
Understanding Heart Disease Risks
Heart disease is often overlooked as a serious health concern, yet it is the leading cause of death in the United States. Many patients fail to recognize the risks associated with cardiovascular disease, often thinking it affects only the elderly. However, the truth is that heart damage can accumulate from a young age. Education on cardiovascular health should begin early, focusing on key indicators like blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and lifestyle choices that contribute to long-term heart health. Understanding these risks can empower individuals to take preventive measures and make informed decisions regarding their health.
Moreover, statistics show that cardiovascular disease claims more lives each year than all cancers combined, a fact that should prompt immediate action rather than complacency. Regular check-ups and awareness of one’s ‘numbers’—including LDL cholesterol and blood pressure—are crucial steps in mitigating risks. Cardiovascular health tips emphasize the need for lifestyle modifications, like a balanced diet low in saturated fats and regular exercise, to maintain optimal heart function and prevent heart disease.
The Importance of Heart Disease Prevention
Preventing heart disease is critical in addressing one of the country’s most pressing health crises. Experts in cardiology underscore the necessity of proactive health measures, and planting seeds of awareness surrounding cholesterol levels has become paramount. For many patients, understanding how to prevent heart disease involves a deeper comprehension of their health metrics, including their cholesterol levels. Promoting cholesterol awareness among the general populace will help to dismantle myths surrounding statins and other cholesterol-lowering medications, making it clear that early intervention can significantly enhance one’s quality of life.
Additionally, initiating conversations around heart disease prevention can inspire individuals to take charge of their health before symptoms manifest. Cardiovascular disease statistics can serve as a wake-up call; they reveal that heart problems don’t just appear suddenly, but often develop due to years of neglecting heart health. Patients are encouraged to understand their risk factors and recognize that prevention is not just about medication, but also about lifestyle choices, regular screenings, and consultations with health professionals.
The Role of Lifestyle in Cardiovascular Health
Lifestyle choices play a pivotal role when it comes to cardiovascular health. It is essential for individuals to engage in regular physical activity, maintain a healthy diet, and manage stress effectively. Exercise not only aids in maintaining a healthy weight but also strengthens the heart itself, reducing the likelihood of developing problems such as high cholesterol and hypertension. Incorporating daily habits that promote heart health can create a ripple effect, influencing overall well-being and longevity.
Moreover, dietary habits are equally significant in preventing heart disease. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats has been linked to improved heart health. Understanding how heart-healthy foods can effectively lower cholesterol levels and encourage better cardiovascular function is key. Patients should strive to minimize processed foods and sugars that can lead to weight gain and increased cholesterol levels, thereby promoting sustainable heart health.
The Impact of Medication on Heart Health
When it comes to managing cardiovascular health, medications, particularly statins, play a critical role in controlling cholesterol levels. Many patients harbor skepticism about the need for statins, often due to misconceptions surrounding their use. However, studies demonstrate that statins can significantly lower LDL cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke. It’s essential to debunk the myths and underscore that these medications, combined with lifestyle changes, can be a powerful tool in heart disease prevention.
Conversely, the underutilization of prescribed medications is an alarming trend witnessed among patients. Factors such as forgetfulness, the complexity of treatment regimens, or mistrust in the healthcare system can hinder individuals from adhering to their medication schedules. To improve adherence, healthcare professionals recommend strategies such as routine follow-ups and the use of ‘navigators’ who can provide personalized support in managing medications and addressing any concerns patients may have regarding their treatment options.
Emerging Technologies in Cardiovascular Treatment
The landscape of cardiovascular treatment is rapidly evolving, with emerging technologies revolutionizing patient care. Techniques such as using machines to keep donor hearts beating during transplants are enhancing recovery times and outcomes for patients. These innovations not only showcase the power of medical advancement but also emphasize the importance of timely treatment for serious heart conditions. Learning about these breakthroughs is fundamental for patients and can inspire them to take their heart health seriously.
Furthermore, wearable fitness devices have become instrumental in promoting cardiovascular health awareness. These technologies provide patients with real-time data on their physical activity, heart rate, and other health metrics, encouraging them to stay informed about their cardiovascular health. By utilizing these advancements, individuals can empower themselves to make healthier lifestyle choices, track their progress, and ultimately prevent heart disease more effectively.
Navigating the Path to Better Heart Health
Navigating the journey towards better heart health can be daunting, especially with the multitude of information available. It is crucial for individuals to engage actively with their healthcare providers about their cardiovascular health concerns. Understanding how to ‘know your numbers’ can greatly influence one’s attitude toward heart health. Rather than waiting for a crisis, proactive engagement in healthcare discussions can yield beneficial outcomes and assist in crafting personalized prevention plans.
Additionally, the use of navigators—health professionals dedicated to guiding patients through their healthcare journey—can bridge the gap between patients and the medical system. They can assist in scheduling appointments, understanding treatment plans, and overcoming barriers to accessing care. This comprehensive support system fosters an environment where patients feel empowered to seek the care they need, ultimately leading to improved heart health outcomes.
Addressing the Underserved Population in Heart Disease
Heart disease does not discriminate; it can affect anyone, but certain populations are disproportionately impacted due to socio-economic factors. Awareness campaigns and outreach programs are essential to educate individuals in underserved communities about heart disease risk factors and prevention strategies. By tailoring these programs to meet the needs of diverse populations, health organizations can ensure that vital information on cholesterol awareness and cardiovascular health tips reaches those who need it most.
Moreover, community-based initiatives can help lower barriers to accessing healthcare, providing resources and support for individuals who may otherwise overlook their cardiovascular health. By promoting preventive measures and screenings within these communities, healthcare providers can combat the rising prevalence of heart disease and reduce disparities in health outcomes. Comprehensive strategies that include dietary programs, exercise classes, and health screenings can empower these populations to take charge of their heart health.
The Future of Heart Health Innovations
As we look to the future, innovations in heart health continue to shape the landscape of preventive medicine and treatment. Advancements in artificial intelligence and personalized medicine hold tremendous potential for enhancing patient care. By leveraging vast amounts of medical data, healthcare providers can tailor treatments and prevention strategies to the individual needs of patients, shifting the paradigm from reactionary care to proactive health management.
Additionally, the development of new medications aimed at cholesterol management is on the rise, focusing on optimized treatment protocols to better serve patients. These innovations not only promise improved health outcomes but also encourage a culture of awareness around cholesterol awareness and prevention. By adopting cutting-edge technologies and strategies, we can transform the way we view cardiovascular health and encourage better practices for heart disease prevention across the population.
Transforming Attitudes Towards Cardiovascular Care
Transforming the perception of cardiovascular disease is imperative for effective prevention strategies. Many patients exhibit a casual attitude towards their heart health, often waiting for symptoms to manifest before seeking medical help. However, altering this mindset is critical; individuals need to embrace a proactive approach to their health by regularly monitoring key metrics such as cholesterol levels and blood pressure. Making heart health a priority rather than an afterthought can significantly reduce the devastating impact of cardiovascular disease.
Healthcare professionals play a pivotal role in this transformation by effectively communicating the risks associated with heart disease and emphasizing the need for early intervention. Programs aimed at educating patients about the serious implications of ignoring heart health are essential. By encouraging dialogues around lifestyle changes, medication adherence, and the significance of regular check-ups, we can foster a culture of understanding that underscores the importance of heart disease prevention.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the best ways to prevent heart disease?
To prevent heart disease, focus on maintaining a healthy diet, staying physically active, and managing risk factors like high cholesterol. Regular check-ups to monitor your cardiovascular health and awareness of cholesterol levels are crucial for early intervention.
How can cholesterol awareness help prevent heart disease?
Cholesterol awareness is vital for preventing heart disease. By knowing your LDL (bad cholesterol) and HDL (good cholesterol) levels, you can make informed lifestyle choices and discuss with your doctor whether medications, like statins for cholesterol, are necessary.
What are some effective cardiovascular health tips?
Effective cardiovascular health tips include eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, exercising regularly, controlling your weight, and reducing stress. Additionally, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake can significantly lower heart disease risk.
What are the latest cardiovascular disease statistics and their significance in heart disease prevention?
Cardiovascular disease statistics reveal that it remains the leading cause of death in the U.S., emphasizing the urgent need for heart disease prevention. Awareness of these statistics can motivate individuals to prioritize their heart health by adopting healthier lifestyles.
When should I consider taking statins for cholesterol management?
You should consider taking statins for cholesterol management if your healthcare provider advises it, particularly if your LDL cholesterol levels are elevated and you’re at risk for heart disease. Early intervention with statins can help significantly reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
| Key Points | Description | Expert Insight | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the U.S. | Despite advancements in medical technology, heart disease prevention awareness is low. | ||
| Patients often delay lifestyle changes and screenings. | Many patients believe they are safe and ignore preventative measures, waiting for symptoms to appear. | ||
| Awareness of LDL cholesterol and other health metrics is crucial. | Knowing their numbers can encourage patients to take preventive actions earlier in life. | ||
| Innovations in cardiovascular treatments are improving outcomes. | Techniques like heart transplant machines and endoscopic surgeries enhance recovery times. | ||
| Patient engagement is essential for effective treatment. | Using navigators and wearable technology can help patients adhere to treatment and monitoring. | ||
Summary
Heart disease prevention should be a top priority for everyone, as it is the leading cause of death in our society. The importance of proactive measures, such as maintaining healthy cholesterol levels and engaging in regular screenings, cannot be overstated. By taking charge of your health and being informed about cardiovascular risks, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing heart disease. With new treatments and technologies emerging, it is essential to stay educated and motivated in the fight against heart disease.

Stem Cell Therapy: New Hope for Corneal Repair
Stem cell therapy is a revolutionary approach that holds great promise for treating conditions that were once deemed incurable, such as severe corneal injuries. Recent advancements in eye treatment have led to the development of cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells, or CALEC, which are derived from healthy eye tissue and successfully transplanted into damaged corneas. This innovative treatment not only provides hope for vision restoration but also demonstrates over 90% effectiveness in clinical trials, changing the lives of patients suffering from limbal stem cell deficiency. The ability to safely restore the cornea’s surface presents exciting prospects for future applications of stem cell therapy in ocular medicine. As research progresses, the potential for regenerative therapies like CALEC will likely expand, paving the way for new methodologies in corneal repair and beyond.
The field of regenerative medicine, particularly through the use of stem cell solutions, is transforming the landscape of eye care. Innovative techniques, such as transplanting cultivated limbal stem cells, are emerging as viable options for individuals grappling with vision loss due to traumatic corneal damage. These advanced therapies, including the promising CALEC surgery, highlight the potential of harnessing the body’s own cellular components to restore both function and quality of life. As scientists continue to explore and refine these methods, the framework for future eye treatments will undoubtedly become more robust, offering patients a new lease on vision and hope in their ability to recover from debilitating eye conditions.
Understanding CALEC Surgery for Corneal Repair
CALEC surgery, or cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells surgery, represents a groundbreaking innovation in the realm of ocular medicine. This advanced procedure involves extracting limbal stem cells from a patient’s healthy eye, which are then cultivated and expanded into cellular grafts. These grafts are subsequently transplanted into the damaged cornea, establishing a new surface of healthy cells that promotes healing and restores vision. With the ability to achieve over 90 percent effectiveness in clinical trials, CALEC surgery offers renewed hope for those suffering from previously untreatable corneal injuries.
The success of the CALEC surgery hinges on the quality of the limbal stem cells and the precision of the transplantation process. Once harvested, the stem cells undergo a sophisticated manufacturing process that adheres to stringent quality standards. This meticulous approach not only ensures the graft’s safety and efficacy but also paves the way for possible future applications, including an allogeneic approach where stem cells from cadaveric donors could expand access to this life-changing treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is stem cell therapy and how does it relate to corneal repair?
Stem cell therapy involves using stem cells to regenerate damaged tissues. In the case of corneal repair, cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells (CALEC) are used to restore the cornea’s surface. This innovative therapy has shown over 90% effectiveness in clinical trials, providing new hope for patients with severe cornea injuries that were previously considered untreatable.
How does CALEC surgery utilize stem cells for vision restoration?
CALEC surgery uses stem cells extracted from a healthy eye to create a graft that is transplanted into a damaged eye. This process aims to regenerate limbal stem cells, which are crucial for maintaining a healthy cornea. The surgery has demonstrated significant success in restoring the cornea’s surface and improving vision in trial participants.
What advancements in eye treatment are associated with stem cell therapy?
Recent advancements in eye treatment, particularly stem cell therapy, include CALEC surgery, which has been successful in regenerating corneal surfaces for patients with limbal stem cell deficiency. These breakthroughs represent significant progress in the field of ophthalmology, potentially transforming the prospects for vision restoration in those with corneal damage.
What are limbal stem cells and why are they important in stem cell therapy for the eye?
Limbal stem cells are specialized cells located at the limbus of the eye that maintain corneal health by supporting its surface. In stem cell therapy, these cells can be cultivated and transplanted to repair corneas that have been damaged due to injuries or diseases. Their restoration is crucial for effective vision rehabilitation.
Are there any risks associated with stem cell therapy for corneal repair?
While stem cell therapy, specifically CALEC surgery, has shown a high safety profile with minimal serious adverse events, there are some risks involved. Potential complications may include minor infections or issues related to the surgical process. Ongoing studies aim to further assess safety and effectiveness long-term as this treatment advances.
Is stem cell therapy for corneal repair available to patients immediately?
Currently, stem cell therapy for corneal repair, such as CALEC surgery, is still experimental and not widely available. Additional studies are needed to support its FDA approval. Researchers are hopeful that larger trials will pave the way for the treatment to become accessible to patients in the future.
Who is conducting research on stem cell therapy for vision restoration?
Research on stem cell therapy for vision restoration, particularly CALEC surgery, is being conducted by a team at Mass Eye and Ear, including principal investigator Ula Jurkunas. This research collaborates with notable institutions like Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Boston Children’s Hospital, underscoring a multidisciplinary approach to advancing eye treatment.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Initial Development | Stem cell therapy CALEC was developed to restore corneal surfaces in patients with blinding injuries. |
| Clinical Trial | Conducted at Mass Eye and Ear, involved 14 patients over 18 months. |
| Effectiveness | Over 90% effective in restoring corneal surfaces, with 79% and 77% complete success rates at 12 and 18 months respectively. |
| Procedure | Involves harvesting stem cells from a healthy eye, creating tissue grafts, and transplanting them into the damaged eye. |
| Safety Profile | No serious adverse events reported; one bacterial infection recorded in a participant. |
| Future Prospects | Research aims to develop allogeneic manufacturing to treat patients with damage in both eyes. |
| Ongoing Research | Further trials and studies are needed to seek FDA approval and ensure wider patient access. |
Summary
Stem cell therapy represents a groundbreaking approach to treat corneal damage that was previously deemed untreatable. The recent clinical trial at Mass Eye and Ear demonstrated that cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells (CALEC) could restore corneal surfaces in a significant percentage of patients, with promising effectiveness and safety outcomes. This advancement illustrates the potential of stem cell therapy not only in ophthalmology but also positions it as a revolutionary treatment methodology for various forms of regenerative medicine.

Plant-Based Oils: A Swap to Boost Longevity by 17%
Plant-based oils, such as olive oil, canola oil, and soybean oil, are increasingly recognized for their impressive health benefits, including the potential to reduce mortality risk. Recent studies reveal that swapping out traditional butter for these healthier oil alternatives can lead to a significant 17% decrease in the risk of premature death. With rising awareness of the health benefits of oils, many are turning to these dietary fat substitutes to enhance their overall well-being. Not only do plant-based oils provide essential fatty acids, but they also contribute to heart health and lower the chances of chronic diseases. Embracing plant-based oils as a versatile butter alternative in your diet could promote longevity and support a healthier lifestyle.
The incorporation of vegetable oils into our diets not only serves as a healthier alternative to butter but also plays a crucial role in enhancing our nutritional profile. By utilizing these liquid fats, one can significantly improve heart health and decrease the risk of conditions related to high mortality rates. The health advantages of oils derived from plants cannot be overstated, especially as more research highlights their positive impact on longevity and disease prevention. Transitioning from solid fats to these liquid dietary fat substitutes offers a practical approach to achieving better health outcomes. Thus, exploring various oil options can provide an enriching experience while promoting well-being.
The Impact of Plant-Based Oils on Health
Plant-based oils have been shown to provide numerous health benefits, particularly when used as a substitute for butter. Rich in unsaturated fatty acids, these oils can contribute to improved heart health and reduced inflammation. According to a recent study published in JAMA Internal Medicine, replacing just a small amount of butter with oils like olive or canola can lead to a remarkable 17% decrease in the risk of premature death. This significant finding underscores the potential for simple dietary swaps to enhance our overall health and longevity.
In addition to lowering mortality rates, the health benefits of oils extend to chronic disease prevention. For instance, olive oil has long been celebrated for its heart-healthy properties and is a staple in Mediterranean diets. The presence of antioxidants in plant-based oils is credited for their protective effects, which may lower the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer and cardiovascular issues. By incorporating more of these oils into our daily meals, individuals can make substantial strides toward a healthier lifestyle.
Butter Alternatives and Their Benefits
As more people embrace healthier eating habits, the demand for butter alternatives has surged. Substituting butter with plant-based oils or margarine can provide similar culinary benefits while significantly reducing saturated fat intake. The health implications of continually consuming high levels of saturated fats from butter can be dire, including increased susceptibility to heart disease and higher mortality rates. Therefore, switching to plant-based oils not only caters to dietary preferences but is also a proactive measure for sustaining better health.
Furthermore, the introduction of dietary fat substitutes allows individuals to enjoy the flavors and textures they crave without compromising their health. Products made from blends of plant-based oils can often mimic the creamy consistency of butter while providing essential fatty acids. This shift toward healthier cooking fats, such as avocado or coconut oil, not only supports better nutrition but also aligns with growing trends in sustainability and plant-based diets.
Reducing Mortality Risk Through Dietary Changes
The substantial connection between diet and health has long been established, but new research highlights how specific dietary changes can significantly reduce mortality risk. According to studies, replacing butter with healthier fats such as plant-based oils can lower a person’s chance of premature death by up to 17%. This statistic emphasizes the importance of evaluating dietary habits and making informed decisions to enhance one’s health longevity.
Moreover, the health benefits of oils serve as a crucial focal point for public health initiatives. By educating individuals on the significance of reducing butter intake and adopting plant-based oils instead, health professionals can potentially decrease the incidence of lifestyle-related diseases. These preventative measures can translate into enormous benefits, creating a healthier population overall and thereby reducing the burden on healthcare systems.
Exploring Olive Oil Benefits in Depth
Among the various plant-based oils, olive oil stands out due to its extensive health benefits. Rich in healthy monounsaturated fats and antioxidants, olive oil not only helps to lower cholesterol levels but is also associated with longevity. Research suggests that incorporating this oil can provide anti-inflammatory properties, which are vital for preventing chronic diseases like heart disorders and certain types of cancer. As a staple in Mediterranean diets, its usage can serve as an excellent alternative to butter in many culinary applications.
Additionally, regular consumption of olive oil has been linked to improved cognitive function and decreased risk of neurodegenerative diseases. Studies have highlighted its role in protecting against Alzheimer’s disease, showcasing how dietary fat substitutes can go beyond basic health benefits and potentially influence quality of life on a broader scale. This highlights the importance of promoting and integrating olive oil into everyday cooking as a means of supporting overall health.
Understanding the Science of Dietary Fats
The science behind dietary fats is intricate, but what is clear is the distinction between saturated and unsaturated fats. Saturated fats, predominantly found in butter, can raise harmful cholesterol levels, leading to increased cardiovascular risks. In contrast, unsaturated fats from plant-based oils provide essential fatty acids that support heart health and overall bodily functions. Engaging with this scientific understanding allows individuals to make informed dietary choices that reflect their health goals.
Research continues to show that dietary fat substitutes play a critical role in preventing chronic health conditions. Factors like heart disease and diabetic outcomes can greatly improve by simply shifting from butter to plant oils rich in omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. This evidence-driven approach emphasizes that small increments in our daily dietary habits—such as the elimination of butter and adoption of healthier oils—can carry profound implications for our long-term health.
The Role of Dietary Surveys in Research
Dietary surveys and long-term studies, like those conducted by Mass General Brigham, are essential in understanding the relationship between diet and health outcomes. By collecting extensive data from large cohorts over decades, researchers can identify trends that correlate with specific dietary patterns. This data is pivotal in forming guidelines that advise public health nutritional strategies aimed at reducing overall mortality risks.
Additionally, these longitudinal studies enable a comprehensive analysis of dietary habits and their impacts on health markers. They underscore the potential long-term benefits of dietary changes, such as substituting butter with healthier fats. With accurate data, researchers can make stronger recommendations that resonate with the general public’s lifestyle, enhancing the effectiveness of health interventions.
Plant-Based Oils: A Key to Healthy Cooking
One major advantage of incorporating plant-based oils into cooking is their versatility and health benefits. These oils can be used in a variety of culinary applications – from frying and baking to dressing salads and marinades. By adjusting recipes to include these oils, individuals can maintain familiar flavors while ensuring a healthier outcome. The shift to oils like avocado, coconut, and olive not only improves dishes nutritionally, but also aligns with modern health-conscious trends.
Moreover, the culinary world has recognized the merits of plant-based oils, leading to innovative dishes that emphasize their health benefits. Chefs and home cooks alike are discovering that these oils can enhance flavor profiles while contributing to a heart-healthy diet. As awareness of nutritional factors grows, so does the opportunity to utilize plant-based oils creatively, promoting a healthier lifestyle without sacrificing enjoyment in cooking.
Long-Term Health Benefits of Dietary Changes
Making long-term changes to dietary habits can yield significant health benefits and improve quality of life. Transitioning from butter to plant-based oils is one such adjustment that research indicates can enhance general well-being. The potential for reducing mortality risk by 17% highlights the profound impact that even minor dietary modifications can have over time, emphasizing the importance of integrating healthier cooking fats into daily meals.
Furthermore, the cumulative effect of these dietary changes can lead to heightened awareness and education about nutrition. As individuals become more mindful of their food choices, the ripple effect can encourage healthier eating patterns in families and communities. The long-term health benefits of substituting butter with plant-based oils not only serve individual needs but promote overall public health initiatives aimed at combating chronic diseases.
The Future of Dietary Guidelines
As new research continues to emerge, the need for updated dietary guidelines becomes increasingly evident. The current emphasis on reducing saturated fat intake while promoting healthy fats aligns with the findings on plant-based oils. Health organizations and professionals will need to refine their recommendations to incorporate these insights, making it clear that swapping butter for oils can have long-term health benefits.
Moreover, future studies should focus on the underlying biological mechanisms that explain the health outcomes associated with these dietary fats. Understanding how plant-based oils interact with our body will help create a clearer narrative for dietary guidelines, allowing for more effective public health campaigns. The evolving landscape of nutrition research highlights the necessity of continuous learning and adaptation in promoting healthier dietary practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the health benefits of using plant-based oils instead of butter?
Plant-based oils, such as olive oil and canola oil, offer numerous health benefits compared to butter. A recent study indicates that substituting butter with plant-based oils daily can reduce the risk of premature death by 17%. These oils contain unsaturated fatty acids, which are linked to lower mortality rates from chronic diseases like cancer and cardiovascular issues.
How do plant-based oils impact mortality risk compared to butter?
Research shows that higher consumption of plant-based oils is associated with a 16% lower risk of overall mortality, in contrast to butter, which is linked to a higher mortality risk. By replacing butter with plant-based oils, individuals can significantly improve their health outcomes.
What types of plant-based oils are recommended as butter alternatives?
Some recommended plant-based oils that serve as effective butter alternatives include olive oil, soybean oil, and canola oil. These oils not only enhance flavor in cooking but also provide essential health benefits, contributing to lower mortality risk.
What dietary fat substitutes can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases?
Dietary fat substitutes like plant-based oils are crucial for reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Studies suggest that incorporating oils such as olive, soybean, or canola into the diet, while reducing butter consumption, can result in significant health improvements.
Are olive oil benefits significant in terms of health improvements?
Yes, olive oil benefits are noteworthy. This plant-based oil is rich in monounsaturated fats and antioxidants, which promote heart health and reduce cancer risks. Incorporating olive oil as a substitute for butter is an effective strategy for enhancing health and longevity.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Findings | Replacing butter with plant-based oils can lower the risk of premature death by 17%. |
| Types of Oils | Soybean, canola, and olive oil are particularly beneficial. |
| Butter’s Impact | Consumption of butter is linked to increased risk of mortality. |
| Study Methodology | Data from 221,054 participants over 30 years analyzed. |
| Health Recommendations | Even minor reductions in butter with an increase in plant oils can lead to health benefits. |
| Future Research | Further studies needed to explore biological mechanisms. |
Summary
Plant-based oils have emerged as a crucial dietary element that can significantly enhance health outcomes. By replacing butter with plant-based oils in your daily diet, you not only enjoy the rich flavors they add to your meals but also reduce your risk of premature death. The recent study highlights that this simple swap can lead to a remarkable 17% reduction in mortality risk, offering a clear and beneficial choice for those aiming for a longer and healthier life.

Medical Gaslighting: Understanding the Impact on Patients
Medical gaslighting is a troubling phenomenon that increasingly affects patients facing persistent or hard-to-diagnose illnesses. When doctors dismiss a patient’s concerns or suggest that symptoms are merely psychological, it can lead to feelings of invalidation and despair. This issue not only disrupts doctor-patient relationships but also significantly impacts mental health, particularly for those enduring chronic illnesses. Empathy in healthcare is crucial, as patients need affirmation and understanding from their providers to manage their health journeys. Recognizing and addressing medical gaslighting can foster more compassionate healthcare environments, ultimately improving outcomes for patients.
Often referred to as ‘medical invalidation,’ medical gaslighting encompasses the dismissive attitudes or statements made by healthcare professionals towards patients. This lack of recognition can occur during doctor visits, where patients feel unheard or misunderstood, particularly regarding complex or invisible conditions. The resulting strain can damage trust in the very relationships designed to provide care and support. Enhancing empathy in healthcare is pivotal, allowing patients to feel validated and respected, which is especially important in the context of chronic health challenges. Addressing these issues openly can help bridge the gap between patients and providers, promoting a more positive healthcare experience.
Understanding Medical Gaslighting and Its Impact on Patients
Medical gaslighting refers to the experience where healthcare providers unintentionally dismiss or invalidate a patient’s concerns, often leading to feelings of confusion and frustration. Patients suffering from chronic illnesses, such as fibromyalgia or long COVID, may frequently encounter situations where their symptoms are met with skepticism, a response that can perpetuate their suffering. This phenomenon intensifies the challenges faced by those dealing with hard-to-detect conditions, amplifying feelings of isolation and helplessness as they navigate the healthcare system.
The ramifications of medical gaslighting extend beyond immediate distress; they can have long-term effects on a patient’s mental health and overall well-being. When individuals consistently feel invalidated, their trust in healthcare providers may diminish, creating barriers to effective communication in doctor-patient relationships. This erosion of trust can prompt patients to delay seeking medical attention or even avoid it altogether. Understanding the dynamics of medical gaslighting is essential for promoting empathetic healthcare practices that recognize the complexities of chronic illnesses.
The Role of Empathy in Doctor-Patient Relationships
Empathy in healthcare is a crucial component that fosters effective communication and meaningful connections between doctors and patients. When providers take the time to listen and validate patients’ concerns, it can significantly reduce feelings of medical invalidation. Empathetic engagement creates an environment where patients feel safe to share their experiences and symptoms, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and treatment outcomes. Ensuring that healthcare professionals are trained in empathetic communication can help mitigate the risks of medical gaslighting.
Furthermore, empathy acts as a protective factor against burnout in healthcare providers. When doctors actively engage in empathetic listening and validation, it can lead to a more satisfying patient interaction, fostering a cycle of positive reinforcement. Providers who feel a connection with their patients are more likely to approach their cases with openness and curiosity, counteracting the pressures that arise from high caseloads and administrative burdens in modern medical practices.
Addressing Medical Invalidation in Healthcare Systems
Addressing medical invalidation requires systemic changes that prioritize compassionate care and adequate provider support. Healthcare systems often impose heavy workloads on medical professionals, which can lead to rushed appointments and superficial interactions. It is essential for healthcare organizations to recognize the impact of these pressures on both patients and providers. By restructuring workflows and emphasizing the importance of patient-centered care, systems can reduce instances of medical invalidation, allowing more room for empathetic conversations.
Moreover, creating awareness about medical invalidation among healthcare professionals is vital. Training programs focused on enhancing communication skills and empathetic engagement can help clinicians recognize signs of patient distress and validate their experiences effectively. Such initiatives can bridge the gap in doctor-patient relationships, fostering an atmosphere of trust and collaboration that is necessary for successful treatment of chronic illnesses.
The Psychological Effects of Medical Gaslighting
The psychological effects of medical gaslighting can be profound, often leading patients to internalize their symptoms as being ‘in their head’ rather than a legitimate health issue. This form of invalidation not only contributes to feelings of distress but can exacerbate existing mental health conditions. Patients may develop anxiety or depression when their physical suffering is dismissed, feeling as if they must fight not only their ailments but also for recognition of their pain within the healthcare system.
Furthermore, the emotional toll of navigating a healthcare environment that frequently invalidates patient experiences can lead to mistrust toward medical professionals. This struggle can create a cycle where patients avoid seeking help due to fear of further invalidation, which can ultimately worsen their conditions. Recognizing and addressing the psychological impacts of medical gaslighting is crucial for improving overall patient health and fostering a more supportive healthcare environment.
Challenges in Chronic Illness Diagnosis
Diagnosing chronic illnesses can be a daunting challenge for both patients and healthcare providers. Conditions like irritable bowel syndrome or chronic fatigue syndrome often elude clear diagnostic criteria, leaving patients feeling vulnerable and dismissed. This difficulty in diagnosis can inadvertently lead to medical gaslighting when providers suggest that symptoms are exaggerated or fabricated, often leading to patient frustration and disengagement from the healthcare process.
Moreover, the complexity of chronic illnesses means that healthcare providers need to approach each case holistically, considering both physical and psychological components. However, systemic pressures within healthcare settings can emphasize quick diagnoses over thorough explorations of symptoms. This neglect can undermine the trust needed in doctor-patient relationships, making it all the more important to adopt a patient-centered approach that prioritizes validation and comprehensive care.
Enhancing Communication Skills in Healthcare Providers
Improving communication skills among healthcare providers is essential to combat the issue of medical gaslighting. Training workshops focused on active listening and empathetic engagement can empower providers to connect more effectively with patients, ensuring their concerns are heard and validated. By fostering a culture of open dialogue, healthcare settings can mitigate feelings of invalidation that many patients experience, ultimately improving their health outcomes.
Additionally, encouraging healthcare professionals to share their difficulties in understanding complex patient cases can contribute to a more collaborative environment. When providers openly express uncertainty and engage in discussions with patients about their symptoms, it can help rebuild trust and encourage a partnership in the patient’s health journey. Enhancing communication also equips healthcare providers to better navigate stressful environments, leading to reduced burnout and more compassionate care.
The Intersection of Mental Health and Chronic Illness
The intersection of mental health and chronic illness presents a unique challenge in healthcare. Many patients suffering from chronic conditions are also at risk of developing mental health disorders, such as anxiety and depression. This delicate relationship often gets overlooked within traditional healthcare frameworks, contributing to cycles of medical invalidation. Patients may already feel vulnerable due to their physical ailments, and when these issues are compounded with mental health struggles, it can lead to feelings of isolation.
Addressing this intersection requires a holistic approach in healthcare that recognizes the importance of mental well-being alongside physical health. Providing patients with access to mental health resources and fostering environments where they can openly discuss both aspects of their health can result in more comprehensive and compassionate care. By integrating mental and physical health services, healthcare systems can better support patients facing the difficulties of managing chronic illnesses.
The Need for Systemic Change in Healthcare
Aside from individual training and awareness, there is a pressing need for systemic change within healthcare to effectively address medical gaslighting and invalidation of patients. This includes reevaluating the metrics by which healthcare providers are evaluated, moving away from productivity-based models to those that value quality of patient interaction and outcomes. When healthcare systems prioritize efficient documentation over genuine patient engagement, it deprives both parties of meaningful interactions.
Implementing policy changes that foster a supportive environment for both providers and patients is essential for combating the pressures that lead to medical gaslighting. Creating interdisciplinary teams where mental health professionals collaborate with physicians can offer a more integrated approach to patient care, ensuring that all aspects of a patient’s health are considered, therefore reducing the likelihood of invalidation and fostering a culture of empathy in healthcare.
Strategies for Patients to Combat Medical Gaslighting
For patients who believe they have experienced medical gaslighting, there are several strategies to advocate for themselves. First and foremost is maintaining a clear record of their symptoms, medical history, and any interactions with healthcare providers. This documentation empowers patients to present clear, well-supported accounts of their experiences, contributing to a more constructive dialogue with healthcare professionals.
Additionally, seeking second opinions or asking for referrals to specialists when concerns are dismissed can help patients find an empathetic provider who recognizes their condition. Joining support groups and connecting with others who have had similar experiences can also provide validation and encouragement. By actively engaging in their own healthcare, patients can work toward dismantling the barriers created by medical invalidation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is medical gaslighting and how does it affect doctor-patient relationships?
Medical gaslighting refers to the experience of patients feeling dismissed or invalidated by healthcare providers when their symptoms cannot be easily explained or diagnosed. This can severely undermine doctor-patient relationships, leading to a breakdown in trust and communication as patients may feel that their concerns are not taken seriously or are attributed to psychological issues rather than legitimate medical conditions.
How can medical gaslighting lead to feelings of invalidation in patients with chronic illnesses?
Patients with chronic illnesses often deal with complex, hard-to-diagnose symptoms that can be misunderstood or minimized by doctors. When healthcare providers express skepticism or attribute symptoms to mental health issues without thorough exploration, it can create a sense of medical invalidation, making patients feel unheard and unsupported in their health journey.
What role does empathy in healthcare play in preventing medical gaslighting?
Empathy in healthcare is crucial for developing meaningful doctor-patient relationships. When healthcare providers actively listen and validate a patient’s experiences, it reduces the likelihood of medical gaslighting. By fostering an atmosphere of understanding and collaboration, providers can better address patient concerns and improve overall health outcomes.
How can patients protect themselves from medical gaslighting during doctor visits?
To protect yourself from medical gaslighting, come prepared with specific details about your symptoms, and be assertive in sharing your experiences. If a provider dismisses your concerns, don’t hesitate to seek a second opinion or ask for further tests. Building a relationship with empathetic providers who respect your input can also help prevent feelings of invalidation.
Is there a distinction between medical gaslighting and medical invalidation?
Yes, there is a distinction. Medical gaslighting often implies intent to deceive or manipulate a patient into doubting their experiences. In contrast, medical invalidation refers to behaviors that may unintentionally dismiss a patient’s symptoms due to provider pressures or biases without malicious intent. Recognizing the difference can help improve understanding and communication in healthcare settings.
What can healthcare systems do to minimize medical gaslighting and enhance doctor-patient relationships?
Healthcare systems can reduce medical gaslighting by investing in training that emphasizes empathy, communication skills, and adequate time for patient interactions. Reducing administrative burdens on physicians can also help them engage more meaningfully with patients, allowing for better recognition and validation of patient concerns, especially in cases of chronic illness.
How does mental health awareness intersect with issues of medical gaslighting?
Mental health awareness is crucial as many patients experiencing medical gaslighting might be labeled with psychological explanations for their symptoms. By increasing awareness of both physical and mental health issues, healthcare providers can adopt a more holistic approach that validates the patient’s experience and addresses both aspects without dismissing physical symptoms as ‘all in the head’.
What are some emotional impacts of medical gaslighting on patients?
Experiencing medical gaslighting can lead to various emotional impacts, including anxiety, depression, and diminished self-worth. Patients may begin to doubt their perceptions and experiences, leading to increased frustration and distrust in the healthcare system, which can compound their original health issues.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Medical gaslighting refers to patients feeling dismissed by healthcare providers about hard-to-detect conditions or symptoms. |
| Patients may be told there’s no medical cause for their symptoms, leading to feelings of invalidation. |
| The term gaslighting suggests intent to deceive, but many cases of medical dismissiveness are unintentional. |
| Increased caseloads and pressure on physicians may contribute to instances of medical invalidation. |
| Psychologist Alexandra Fuss advocates for recognizing unintentional invalidation rather than labeling it as gaslighting. |
| Improved patient-provider interactions could result from addressing systemic pressures on healthcare professionals. |
Summary
Medical gaslighting is a significant issue in healthcare, affecting patients who feel dismissed by their doctors, particularly regarding complex medical conditions. Many healthcare providers inadvertently contribute to this issue due to the overwhelming pressures they face, including high caseloads and extensive documentation requirements. Alexandra Fuss suggests that reframing our understanding of such dismissive behavior as ‘medical invalidation’ rather than ‘gaslighting’ may foster greater empathy towards healthcare providers and improve patient-care dynamics. By acknowledging the systemic challenges within healthcare, we can work towards enhancing communication and trust between patients and their doctors, ultimately leading to better healthcare experiences.

Airborne Disease Control: How Personality Hindered Progress
Airborne disease control is a critical aspect of public health that seeks to mitigate the spread of infectious diseases transmitted through the air. With the rise of airborne pathogens, understanding the mechanisms of disease transmission has never been more crucial. Experts like Carl Zimmer highlight the historical significance of researchers like William Firth Wells, whose groundbreaking work paved the way for our understanding of how germs can infiltrate the air we breathe. Despite the challenges posed by misconceptions rooted in the old germ theory, Wells’ pioneering experiments demonstrated the importance of recognizing airborne routes of infection. As we navigate the complexities of airborne disease control, a comprehensive approach is essential to safeguard community health and prevent outbreaks.
The management of diseases that spread through the air, often referred to as airborne infection control, plays a vital role in ensuring public safety. This area encompasses strategies aimed at minimizing the risk of transmission of pathogens that can travel via respiratory droplets or aerosolized particles. Historical milestones, such as those identified by Carl Zimmer in his exploration of figures like William Firth Wells, illuminate the ongoing challenges associated with public acceptance of such scientific advancements. Innovations in our understanding of airborne diseases underscore the need for continued research and education surrounding the pathways of transmission. In an age where airborne illnesses can emerge rapidly, adopting effective airborne pathogen management practices is essential for future health security.
The Legacy of William Firth Wells in Airborne Disease Control
William Firth Wells, often overshadowed by his contemporaries, has been credited with pioneering research in airborne disease transmission. His meticulous studies laid the groundwork for understanding that microorganisms could be present in the air we breathe, fundamentally altering the perception of how diseases spread. Despite his important contributions, Wells struggled against a lack of recognition due to both the science of his time and his uncharismatic presentation style. This serves as a poignant reminder of how even groundbreaking ideas can be dismissed if not communicated effectively.
In his lectures, Wells employed innovative techniques, such as cultivating air samples to isolate pathogens, establishing the relationship between airborne microbes and illness. However, his demeanor often alienated audiences and potential collaborators, contributing to a stifled academic career. Carl Zimmer argues that this interplay between personality and scientific acceptance illustrates a significant barrier in the widespread integration of Wells’ ideas into public health protocols. As contemporary debates focus on airborne disease control, understanding these dynamics becomes crucial in fostering better communication of equally vital research.
The Science of Airborne Pathogens: A Historical Perspective
The discovery of airborne pathogens has a storied history, tracing back to the initial miasma theories of ancient Greece. Hippocrates postulated that illness could be caused by polluted air, a notion that persisted until the 19th century, when Louis Pasteur and others advanced the germ theory of disease. This shift from miasmas to microorganisms was essential in developing effective public health responses to airborne diseases. The skepticism faced by early scientists demonstrates the difficulty in overcoming existing paradigms and highlights the importance of continued education and advocacy within the medical community.
As medical professionals began to embrace germ theory, figures like Wells extended this understanding beyond traditional transmission routes, recognizing the air as a medium for disease. Despite his groundbreaking research, societal hesitance to adapt to novel ideas about airborne diseases has continued to impact public health policies. Understanding the historical context of airborne pathogens enriches our comprehension of current efforts to mitigate disease transmission, emphasizing the need for public and scientific discourse that promotes innovative approaches to health emergencies.
Challenges in Public Acceptance of Airborne Disease Theories
The journey of airborne disease research reveals significant hurdles in achieving public and scientific acceptance, a challenge that still resonates today. Throughout history, scientific breakthroughs have often been met with skepticism, particularly those that contradict widely held beliefs. The idea that diseases could be spread through the air was initially dismissed despite compelling evidence from pioneers like Wells. Public health practitioners faced the daunting task of convincing both policymakers and the general populace of the need to adapt health responses to include airborne transmission risks.
Carl Zimmer’s exploration of this issue elucidates the relationship between scientific discovery and public perception. In the face of emerging threats, such as COVID-19, understanding historical resistance to airborne disease theories can aid in shaping persuasive public health campaigns. Bridging the gap between science and society requires effective communication strategies that address misconceptions and reaffirm the importance of research in developing grounded health interventions.
The Role of Personality in Scientific Advancement
Carl Zimmer’s examination of Wells highlights an intriguing phenomenon in the world of science: the impact of personality on professional success and public acceptance of ideas. Wells, a brilliant mind in the study of airborne pathogens, faced numerous setbacks due to his socially awkward demeanor. While the scientific community often elevates charismatic figures as heroes of discovery, Wells’ story illustrates that exceptional scientific work does not always correlate with personal charm or social likability. This raises questions about how we value scientific contributions and the mechanisms that perpetuate bias in research fields.
Examining the influence of personality sheds light on the broader implications for current and future scientists. For instance, effective communication and collaboration skills are increasingly necessary to navigate an evolving science landscape. Instead of favoring traditional notions of the ‘Great Man’ in history, there is a call to recognize the collaborative nature of scientific endeavor, where the interplay of diverse perspectives can lead to more significant advancements in understanding issues like airborne disease control.
The Impact of Germ Theory on Modern Medicine
Germ theory revolutionized the field of medicine and transformed our approach to infectious diseases, particularly those transmitted through the air. The work of scientific giants such as Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch established the foundation for modern microbiology, allowing healthcare professionals to develop targeted interventions for preventing diseases caused by airborne pathogens. This transition not only changed treatment protocols but also led to the implementation of strict hygiene practices in healthcare settings, reflecting an evolution in how society conceptualizes health.
As a result of these foundational theories, the 20th century saw the emergence of robust public health initiatives aimed at minimizing the spread of infections. Understanding airborne transmission has become increasingly vital as global travel and urbanization facilitate the rapid spread of diseases. Current public health strategies, which incorporate germ theory’s principles, focus on preventive measures such as vaccination programs, improved air quality, and the importance of ventilation in closed spaces, recalling Wells’ own research on airborne pathogens and UV light’s potential to disinfect.
Understanding Disease Transmission: Insights from History
Disease transmission remains a crucial area of study in public health, and reviewing historical models provides valuable insights into our present challenges. For centuries, scientists grappled with inconclusive data regarding how diseases spread. Key moments in history, such as the cholera outbreaks of the 19th century, showcased the reluctance to accept airborne transmission theories. As public health strategies have evolved, lessons learned from historical inaction serve as a guide in addressing contemporary health crises involving airborne pathogens.
Moreover, this understanding reinforces the importance of ongoing research and dialogue in the health community. As future outbreaks arise, referencing the successes and failures of historical disease control measures empowers modern scientists to adapt their strategies. By recognizing the significance of the context and the personalities behind major scientific advancements, we can better equip ourselves to manage emergent threats and promote public trust in science.
Carl Zimmer’s Contributions to Science Communication
Carl Zimmer exemplifies the role of effective science communication in bridging the gap between complex scientific ideas and public understanding. By chronicling the history of airborne disease research, Zimmer brings to light essential discoveries that might otherwise be forgotten, elevating the conversation surrounding public health. His work accentuates the responsibility that scientists hold—not only to conduct research but also to disseminate knowledge in an engaging and comprehensible manner.
The discussions prompted by Zimmer’s insights resonate deeply in today’s society, especially regarding emergent health threats like COVID-19. As scientists navigate the intricacies of disease prevention, the ability to articulate findings clearly is paramount in influencing public behavior. Zimmer’s commitment to making science accessible encourages a culture where informed decision-making can thrive, fostering an environment that values the nuances within the science of airborne diseases and germ transmission.
Current Trends in Airborne Disease Research
As we continue to navigate the complexities of public health, current trends in airborne disease research are increasingly focused on the relationship between environmental factors and disease transmission. Relevant studies are investigating how air quality, ventilation systems, and urban design can contribute to the spread of airborne pathogens, underlining the ongoing relevance of Wells’ work. The resurgence of interest in such research reflects a broader recognition of the need for multidisciplinary approaches to public health.
Researchers are now employing advanced technologies to assess airborne pathogen levels more accurately. This includes the integration of real-time monitoring systems in hospitals and public spaces to identify potential outbreak sources. Understanding and controlling environmental conditions to mitigate disease transmission remain at the forefront of medical research, as communities worldwide seek effective solutions in the face of future pandemics. Such modern methodologies, grounded in historical research, ensure that scientists remain vigilant in combating airborne diseases.
Public Health Policy: Lessons from the Past
The discussions surrounding public health policy often reflect lessons learned from past experiences. The historical context of airborne pathogen research reveals significant implications for contemporary governance and health directives. For instance, examining how Wells’ theories were neglected due to societal biases showcases a need for policies that embrace emerging scientific evidence regardless of the prevailing norms. As nations develop their public health frameworks, prioritizing research, innovation, and stakeholder engagement can enhance resilience against future health threats.
Additionally, effective public health policies must adapt based on emerging evidence, which includes the integration of findings from historical research on airborne diseases. This adaptability enhances our response to ongoing challenges, such as viral outbreaks and antibiotic resistance. By drawing on historical successes and failures, policymakers can develop robust, evidence-based strategies that prioritize community health, ensuring that we learn from the past while innovating for a safer future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role did William Firth Wells play in airborne disease control?
William Firth Wells was a pivotal researcher in airborne disease control, demonstrating that pathogens could be transmitted through the air. His innovative experiments, including cultivating air samples, provided strong evidence supporting this theory, which was essential for understanding disease transmission.
How does air pollution relate to airborne disease control?
Air pollution can exacerbate the spread of airborne pathogens, leading to increased disease transmission. Effective airborne disease control measures often involve improving air quality to reduce the presence of harmful particles and microbes in the air.
What is germ theory and its relevance to airborne disease control?
Germ theory, championed by scientists like Louis Pasteur, established that microorganisms cause diseases. This theory underpins airborne disease control, as it highlights the importance of preventing the spread of airborne pathogens to mitigate infectious diseases.
How can UV light be used in airborne disease control?
UV light has been shown to effectively eliminate airborne pathogens. Research by William Firth Wells demonstrated its potential in disinfecting air, making it a vital tool in airborne disease control strategies, especially in enclosed environments.
Why is the history of airborne pathogens significant for public health?
Understanding the history of airborne pathogens is crucial as it informs current airborne disease control strategies and highlights how historical misconceptions about disease transmission can affect public health policies.
What lessons can be learned from the history of research on airborne disease control?
The history of airborne disease control, including William Firth Wells’ contributions, teaches us that scientific acceptance can be delayed by personality and communication issues. It also underscores the importance of continuing research and innovation in controlling airborne pathogens.
How do modern practices reflect the discoveries related to airborne disease control?
Modern practices in airborne disease control, such as enhanced ventilation systems and the use of UV light for disinfection, are directly influenced by the historical work on airborne pathogens, demonstrating the evolution and application of these scientific discoveries.
What advancements are needed in airborne disease control based on historical research?
Advancements in airborne disease control will benefit from adopting innovative technologies, improving public awareness, and addressing the historical challenges faced by researchers like William Firth Wells to create more effective strategies against airborne threats.
| Key Points | |
|---|---|
| Carl Zimmer’s Theories | Discusses the impact of personality on the acceptance of airborne disease science. |
| William Firth Wells | A key researcher whose dry personality may have hindered advancements in airborne disease control. |
| Historical Context | Theories of disease transmission evolved from miasmas to germs, often overlooking air as a medium for disease. |
| Experiments by Wells | Conducted studies indicating airborne pathogens could spread diseases, yet faced career challenges due to his demeanor. |
| Impact of UV Light | Wells discovered that ultraviolet light could eliminate airborne pathogens. |
| Research and Challenges | Wells’ work was delayed and marginalized, leading to threats in public health during outbreaks. |
| Legacy | Despite impactful research, Wells’ contributions to airborne disease control were largely unrecognized during his life. |
Summary
Airborne disease control is crucial for public health, yet often the scientific progress in this field is hindered by the personalities of researchers connected to it. As illustrated by Carl Zimmer in his exploration of William Firth Wells, an overlooked yet key figure in the history of airborne diseases, personal attributes can significantly affect the acceptance of groundbreaking ideas. Wells’ struggles demonstrate that even vital scientific research on airborne pathogens can stall due to an unlikable persona, emphasizing the need for improving how such science is perceived and accepted by both peers and the public. Understanding the dynamics of personality in scientific communication is essential for advancing effective airborne disease control measures.

U.S. Innovation Ecosystem: A Historical Perspective
The U.S. innovation ecosystem stands as a global leader, rooted in a rich history of collaboration and breakthroughs, particularly in biomedical research. From the mass production of penicillin during World War II to contemporary medical research advancements, this ecosystem thrives on the synergy between public and private sectors. Federal R&D funding has played a pivotal role in supporting this dynamic, fostering partnerships that spur innovation and drive technological progress. As we examine the legacy of federal investment in science, it’s clear that the evolution of public-private partnerships has been instrumental in not only addressing immediate challenges, such as wartime medical needs, but also in laying the groundwork for future discoveries. In doing so, the U.S. has cultivated an environment where science and technology can flourish, maintaining its status as a vanguard in global innovation.
The landscape of U.S. innovation characterized by a robust network of collaborative efforts has become a model admired worldwide. This synergy between private enterprises and government entities emphasizes the importance of financial support in enhancing research capabilities. Notably, historical milestones like the development of antibiotics during the Second World War illustrate how government-backed initiatives can lead to monumental advancements in healthcare. The partnerships formed between federal institutions and the academic community create a resilient framework that supports ongoing exploration and development across various fields. Together, these elements contribute significantly to the dynamic evolution of the innovation economy, underpinning advancements that resonate far beyond U.S. borders.
The Historical Roots of the U.S. Innovation Ecosystem
The U.S. innovation ecosystem is deeply rooted in the history of government and academic partnerships that date back to World War II. It began when scientists and leaders from U.S. universities rallied together to harness their expertise for military advancements, which ultimately transformed medical research. During this period, penicillin was mass-produced for the first time, showcasing the potential that public-private partnerships hold in accelerating biomedical research. This collaboration set the stage for robust federal R&D funding strategies that have persisted through various administrations, continually shaping the landscape of scientific inquiry and innovation.
Today, this innovative alliance remains fundamental as it fosters a culture where academia and industry collaborate closely to address pressing health and technological challenges. As we delve into the pivotal moments of this partnership, it becomes clear that the overlap of resources and knowledge-sharing has been essential in driving medical research advancements that have significant global implications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role does the U.S. biomedical research play in the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
U.S. biomedical research is a cornerstone of the U.S. innovation ecosystem, driving advancements in healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and medical technologies. With robust public-private partnerships supported by federal R&D funding, it promotes significant discoveries and innovations that enhance the health and well-being of the population.
How did the history of penicillin influence the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
The history of penicillin marks a pivotal moment in the U.S. innovation ecosystem, showcasing how government-supported research during World War II led to the mass production of antibiotics. This not only saved countless lives during the war but also laid the groundwork for modern biomedical advancements and the ongoing collaboration between federal agencies and private sector enterprises.
What are the benefits of public-private partnerships in the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
Public-private partnerships are vital in the U.S. innovation ecosystem as they foster collaboration between federal agencies and private entities. This synergy enhances funding for research, accelerates medical research advancements, and leads to innovative solutions to healthcare challenges, benefiting both the economy and society.
How has federal R&D funding shaped the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
Federal R&D funding has significantly shaped the U.S. innovation ecosystem by providing essential financial support for research projects. This funding facilitates breakthroughs in various fields, particularly in biomedicine, and helps build the infrastructure necessary for developing new technologies and treatments.
What lessons can the U.S. innovation ecosystem learn from the penicillin development during WWII?
The development of penicillin during WWII highlights the importance of rapid innovation and collaboration within the U.S. innovation ecosystem. It underscores the need for a coordinated effort between government, academia, and industry to tackle urgent national health challenges through innovative research and technologies.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Origin of the U.S. Innovation Ecosystem | The U.S. innovation ecosystem began during World War II, focusing on mass production of penicillin and establishing a public-private partnership. |
| Impact of Federal Funding | Federal funding has historically supported academic research, leading to innovations in medicine and technology, and is critical for sustaining the ecosystem. |
| Federal-Government and Academia Partnership | This partnership was formalized during WWII for military advancements and has evolved over the decades to support biomedicine and technology. |
| Technological Advancements During WWII | The urgent demand for new technologies during WWII led to significant breakthroughs, particularly in medicine, such as the development of penicillin. |
| Continuation and Growth of the Ecosystem | The U.S. innovation system has continued to flourish due to its foundational achievements and consistent federal support, particularly in health. |
| Current System Overview | Today’s ecosystem consists of universities, life sciences industries, and federal research institutions working collaboratively. |
| Challenge for Future Funding | Recent proposals to cap reimbursements for research may lead to significant funding cuts for biomedical innovations, risking the ecosystem’s stability. |
| The Global Context | The U.S. innovation ecosystem is viewed as a model worldwide, showcasing the effectiveness of government and academic partnerships in driving progress. |
Summary
The U.S. innovation ecosystem is at the forefront of global technological advancements, having evolved from its roots during World War II when government and academia teamed up to tackle urgent health crises. This unique partnership has led to groundbreaking discoveries, particularly in biomedicine, shaping a robust system that continues to thrive today. Federal funding plays a crucial role in this ecosystem, supporting research initiatives that spur innovation and economic growth. However, recent discussions about limiting funding could jeopardize this success, underscoring the importance of maintaining robust support for research. As the world looks to the U.S. for inspiration in fostering innovation, it is vital to protect and promote the mechanisms that have made this ecosystem a global leader.

Is Sugar Addictive? Understanding Its Effects on Health
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked heated debates among nutritionists, researchers, and health enthusiasts alike. While sugar may not meet the strict clinical criteria required to classify it as a true addictive substance like nicotine or alcohol, it undeniably exerts a powerful influence on our cravings and dietary choices. The health effects of sugar, particularly from processed foods and sugar-laden snacks, cannot be overlooked, as they have been linked to increased consumption and dependency-like behaviors. Understanding sugar addiction is crucial as we navigate the complex landscape of reducing sugar intake and maintaining a balanced diet.
Exploring the concept of sugar dependency brings to light various terms and aspects associated with this topic. Some refer to it as sweet tooth syndrome or the compulsion to indulge in sugary treats, which can lead to intense sugar cravings. The influence of processed foods and sugar-laced products complicates our relationship with sweetness, often prompting individuals to seek solace in these high-calorie delights. Understanding the health ramifications connected with excessive sugar consumption is essential, as it can lead to serious medical concerns and challenges in managing one’s diet. Ultimately, recognizing the fine line between moderation and overindulgence in sugary foods can aid in fostering healthier eating habits.
The Addictive Nature of Sugar
The concept of sugar addiction has generated considerable debate among nutrition researchers and health experts. While sugar can stimulate cravings and lead to increased consumption, its classification as an addictive substance is complex. Unlike alcohol or nicotine, which fit stricter clinical criteria for addiction, sugar is found naturally in many foods such as fruits and dairy. This intrinsic presence challenges the notion of total elimination, as removing all sugars would mean cutting vital nutrients from a person’s diet.
Despite not being officially classified as an addictive substance, many individuals report experiencing cravings for sugary snacks, particularly those found in processed foods. These cravings can lead to habitual eating behaviors that mimic compulsive tendencies often associated with traditional addictions. As one increases their intake of ultra-processed foods laden with added sugars, it can exacerbate these compulsive patterns, highlighting the need for careful moderation.
Understanding Sugar Cravings
Sugar cravings often stem from the body’s physiological and psychological responses to high sugar consumption. Foods that are high in added sugars are typically more palatable, making them easier to overconsume. When one indulges in these sugary foods, the brain releases dopamine, creating feelings of pleasure and reinforcing the desire to seek out similar foods in the future. This repetitive cycle of craving and consumption can lead to increased sugar intake, resulting in potential health effects.
Moreover, it’s vital to acknowledge that sugar cravings can also be triggered by emotional factors like stress or boredom. Researchers suggest that understanding the underlying reasons for these cravings can help in managing them effectively. Avoiding restrictive diets that completely eliminate sugar may be more practical; however, educating oneself about portion sizes and reading nutritional labels can empower individuals to make healthier choices without feeling deprived.
Health Effects of Excess Sugar Consumption
Numerous studies have linked high sugar consumption to various health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. The American Heart Association underscores the importance of keeping added sugar consumption within recommended limits: no more than 9 teaspoons for men and 6 teaspoons for women each day. Exceeding these limits can lead to significant calorie intake resulting in weight gain and the risk of developing chronic conditions.
In addition to physical health risks, consuming too much sugar can also lead to psychological impacts such as mood swings and anxiety. Individuals might initially feel a boost of energy after consuming sugary foods, but this is often followed by a crash that can result in fatigue and irritability. Being mindful of how much added sugar one consumes is essential for maintaining both physical and mental well-being.
Distinction Between Natural vs. Added Sugars
It’s crucial to distinguish between natural sugars found in whole foods and added sugars that are incorporated into many processed products. Natural sugars, such as those found in fruits and vegetables, come with additional nutrients and fiber that help regulate blood sugar levels. In contrast, added sugars found in soft drinks, snacks, and desserts offer little to no nutritional value and can lead to overeating, weight gain, and ultimately health problems.
By reading labels carefully and being aware of added sugars, consumers can make more informed decisions about their dietary choices. Opting for whole foods instead of processed ones can help mitigate sugar addiction tendencies, as these foods not only provide natural sweetness but also essential nutrients that support overall health.
Reducing Sugar Intake for Better Health
Reducing sugar intake can be a challenging journey for many, especially for those accustomed to high-sugar diets. Gradually decreasing added sugar consumption is often more sustainable than attempting to quit ‘cold turkey.’ This method allows the body to adjust without experiencing severe withdrawal symptoms associated with drastic dietary changes, such as headaches and fatigue.
Implementing small changes like swapping soda for sparkling water or choosing fruit-based desserts over sugary treats can make a significant difference. Furthermore, meal planning and cooking at home can help individuals control their overall sugar intake, leading to improved health outcomes while maintaining enjoyment in their diet.
The Role of Processed Foods in Sugar Addiction
Processed foods are typically high in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, making them hyper-palatable. This combination not only increases cravings but also promotes habitual consumption, making it difficult for many individuals to manage their sugar intake effectively. The omnipresence of these foods in one’s diet can lead to a slippery slope of increased dependence on sugary snacks and beverages.
By becoming aware of the link between processed foods and sugar intake, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize their consumption. Choosing whole, minimally processed foods can not only reduce sugar cravings but also provide the nutrients necessary for overall health. Understanding the impact of processed foods enables consumers to make healthier choices and foster better eating habits.
Psychological Aspects of Sugar Consumption
The psychological effects of sugar consumption can be profound. For many, sugary foods become a comfort during stressful times, offering temporary relief and pleasures. However, relying on sugar for emotional coping can lead to a vicious cycle of dependency, where one continually seeks out sugar to manage feelings of anxiety or sadness.
Building awareness of these emotional triggers and finding alternative coping mechanisms, such as exercise or mindfulness practices, can significantly reduce one’s reliance on sugary snacks. Working on emotional health can lead to better choices and a healthier relationship with food.
Lifestyle Changes to Curb Sugar Cravings
Making intentional lifestyle changes can significantly help curb sugar cravings. Regular physical activity not only helps to maintain a healthy weight but also boosts mood and reduces stress, lessening the need to rely on sugary foods for emotional comfort. Finding alternative ways to engage in enjoyable activities that occupy one’s time can also decrease cravings.
Moreover, establishing a balanced diet rich in whole grains, proteins, healthy fats, and fiber can stabilize blood sugar levels, further reducing cravings for added sugars. By ensuring meals are nutrient-dense and satisfying, individuals can find themselves less tempted by sugary snacks during the day.
Navigating the Sweetness Spectrum
It’s important to recognize that while sugar does have addictive qualities, it also plays a significant role in enhancing flavor and enjoyment in our diets. The emphasis shouldn’t solely be on eliminating sugar but rather on understanding its place in a balanced diet. Moderation and context are key.
By cultivating a balanced approach towards sweetness—without labeling sugar as entirely bad—individuals can enjoy its benefits within a healthy framework. Focusing on whole foods and mindful eating practices can allow for a satisfying diet that includes some sweetness without detrimental effects on health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive in a way that leads to compulsive eating?
While sugar can lead to sugar cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. Current research suggests that sugar may induce pleasurable feelings, which can create habitual consumption patterns, especially from processed foods.
What are the health effects of sugar consumption related to addiction?
The health effects of sugar can mimic some addictive behaviors, such as increased cravings and withdrawal-like symptoms when cutting back. However, unlike harder drugs, sugar is essential in moderation, as it naturally occurs in many nutrients we need for survival.
How can I deal with sugar cravings if sugar isn’t truly addictive?
To manage sugar cravings effectively, focus on gradually reducing sugar intake instead of going cold turkey. Eating whole foods and being mindful of food labels can help significantly in curbing sugar cravings.
What role do processed foods play in sugar addiction?
Processed foods often contain high levels of added sugar, unhealthy fats, and sodium, making them particularly palatable and easy to overconsume. This habitual consumption can lead to increased sugar cravings, which contribute to the perception of sugar addiction.
Are there strategies for reducing sugar intake without addiction-like withdrawal symptoms?
Yes, reducing sugar intake gradually is the best approach. Incorporating more whole foods and being mindful of serving sizes helps mitigate any potential withdrawal symptoms that may mimic sugar addiction.
Is there a limit to sugar intake to avoid addictive behaviors?
The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar to no more than 9 teaspoons for men and 6 teaspoons for women daily. Staying within these limits minimizes health risks and helps control sugar cravings effectively.
How does sugar fit into a balanced diet without being addictive?
Sugar, when consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet, can enhance flavor and enjoyment of food without leading to addictive behaviors. It’s essential to differentiate between naturally occurring sugars and added sugars from processed foods.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Is sugar addictive? | A highly debated topic; sugar has cravings but not classified as addictive as alcohol or nicotine. |
| Comparison with substances | Substances like alcohol and nicotine are classified as addictive; sugar isn’t, but shares some compulsive eating behaviors. |
| Consumption of sugar | Average American consumes 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily; recommended limits are 9 teaspoons for men, 6 for women. |
| Health effects | Moderate consumption is fine; excessive leads to health issues. Withdrawal-like symptoms may occur with sudden cessation |
| Sugar in diet | Sugar is found in many healthy foods, indicating it’s not entirely harmful if consumed mindfully. |
| Advice on consumption | Reduce sugar intake gradually; read food labels and be mindful of amounts in processed foods. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This question sparks much debate among nutrition experts. While sugar can lead to cravings and certain compulsive eating behaviors, it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. Moderate sugar intake is acceptable and necessary for overall health. It’s vital to be aware of how much sugar we consume, especially from processed foods loaded with added sugars. Understanding and managing sugar consumption can lead to healthier eating habits without needing to treat sugar as a strictly forbidden substance.