Alzheimer’s early detection has emerged as a crucial priority in the fight against this devastating neurodegenerative disease. Innovations in Alzheimer’s diagnosis, like the recently developed at-home olfactory test, present a promising avenue for identifying individuals at risk long before clinical symptoms manifest. This test evaluates the ability to recognize and remember smells, revealing a significant correlation between olfactory dysfunction and early signs of Alzheimer’s. Early intervention through cognitive impairment tests not only paves the way for timely treatment options but also enhances our understanding of neurodegenerative diseases. As research unfolds, such early detection methods could revolutionize how we approach Alzheimer’s, offering hope to countless families affected by this condition.
Recognizing early signs of cognitive decline is essential for proactive healthcare strategies. The advancement of at-home tests designed for the assessment of olfactory function provides a new lens through which we can view the early stages of Alzheimer’s and related disorders. These tests, which focus on smell identification and memory, represent a shift towards more accessible diagnostics outside the clinical setting. By understanding the nuances of cognitive impairment and prioritizing early Alzheimer’s identification methods, caregivers and medical professionals can better aid those at risk. Consequently, such tools do not only signal potential cognitive issues but also reinforce the significance of early intervention in mitigating the progression of neurodegenerative illnesses.
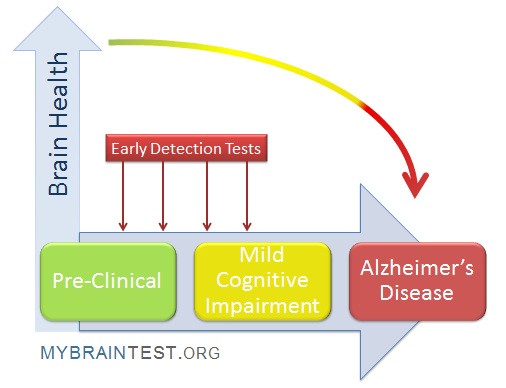
Understanding Alzheimer’s Early Detection
Alzheimer’s early detection is becoming a vital component in the fight against cognitive decline. Researchers are continuously seeking innovative methods to identify individuals at risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease well ahead of the onset of noticeable symptoms. One groundbreaking approach involves olfactory tests that enable at-home evaluations of one’s sense of smell. These tests measure various aspects of olfactory function, including odor identification and discrimination, which, as studies suggest, can be closely linked to cognitive impairment and overall brain health.
By focusing on early detection, healthcare professionals aim to intervene before significant memory loss occurs, potentially slowing down the progression of Alzheimer’s and improving patients’ quality of life. Understanding the nuances of cognitive impairment tests, facilitated by noninvasive methods like the home olfactory test, empowers both patients and providers to be proactive in managing neurodegenerative diseases. Such initiatives represent a promising avenue for Alzheimer’s prevention strategies.
The Role of Olfactory Function in Cognitive Health
Recent research has drawn a compelling connection between olfactory function and cognitive health, particularly in the context of neurodegenerative diseases. Studies suggest that a diminished sense of smell may serve as one of the early signs of Alzheimer’s disease and other cognitive impairments. As older adults often experience natural age-related decline in their olfactory capabilities, it becomes crucial to discern whether these changes indicate a risk for significant cognitive decline.
The innovative home olfactory test developed by Mass General Brigham offers a simple way for individuals to assess their olfactory health and, by extension, their cognitive function. This test not only identifies those who might be at risk but also triggers further investigation into their cognitive status. As the research progresses, integrating olfactory tests into clinical assessments could revolutionize how we identify and manage Alzheimer’s disease.
Cognitive Impairment Tests: A New Frontier
Cognitive impairment tests have traditionally been conducted in clinical settings, often making access difficult for many individuals. The rise of at-home tests, particularly olfactory assessments, presents an exciting and accessible alternative for monitoring cognitive health. Participants can now engage in testing that is both noninvasive and straightforward, allowing for ongoing monitoring of potential early signs of Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases from their homes.
Such advancements in cognitive impairment tests not only help in identifying risks but also empower individuals with vital information about their brain health. By breaking down barriers to access, researchers hope to reach a broader population, identifying risks among diverse demographics, and facilitating earlier interventions that could significantly impact disease trajectories.
Benefits of At-Home Olfactory Tests
At-home olfactory tests offer a multitude of benefits, particularly in the realm of early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. First and foremost, they provide a convenient option for individuals who may have difficulty accessing traditional clinical testing environments. Participants can complete these tests in the comfort of their homes without the need for extensive travel or appointments.
Additionally, the cost-effective nature of these tests makes them an appealing option for wider implementation. As researchers continue to validate their effectiveness, such olfactory tests could emerge as standard tools not only for early Alzheimer’s detection but also for monitoring cognitive health in broader populations. The simplicity and effectiveness of these tests could lead to greater public awareness and proactive health management among aging individuals.
Neurodegenerative Diseases and Early Warning Signs
As we age, the risk of developing neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s increases, making early detection increasingly essential. Researchers are now focusing on uncovering early warning signs, such as olfactory dysfunction, that could signal the onset of cognitive decline. Understanding these signs can lead to timely intervention, which can be crucial in managing the symptoms and progression of such diseases.
By remaining vigilant for signs such as a diminished sense of smell, individuals and healthcare providers can work together to address potential cognitive issues before they escalate. Ongoing research into the relationship between olfactory health and neurological function underscores the importance of such early warning signs in the battle against neurodegenerative conditions.
Exploring Innovative Research Solutions
The search for effective solutions in the realm of Alzheimer’s early detection is opening new avenues for research and innovation. With the promising results of olfactory tests, researchers are actively exploring how such methodologies can be integrated into existing frameworks for early diagnosis and intervention. This includes collaborating with medical professionals to create protocols that utilize these innovative tests on a larger scale.
Furthermore, as studies continue to reveal the connections between cognitive function and sensory capabilities, researchers aim to develop comprehensive strategies that encompass various cognitive impairment tests. Through advanced research techniques, including longitudinal studies, the aim is to continually refine these solutions to better predict and manage Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases.
The Promise of Early Intervention
The prospect of early intervention in Alzheimer’s disease is one of the most promising outcomes of recent research efforts. By employing at-home olfactory tests for early detection, there is a genuine opportunity to offer targeted therapies and lifestyle modifications to those identified at risk. This preemptive approach could delay or even prevent the onset of debilitating cognitive symptoms associated with Alzheimer’s.
Additionally, raising awareness around the importance of early detection could foster a culture of proactive health management among older adults. Parents, caregivers, and families can become informed advocates for regular cognitive health assessments, paving the way for more individuals to engage in preventative strategies that combat neurodegenerative diseases.
The Community Impact of Alzheimer’s Research
Alzheimer’s research, particularly innovations like home olfactory tests, extends beyond individual health benefits; it has profound implications for communities at large. Increased awareness and understanding of Alzheimer’s disease can reduce stigma associated with cognitive decline, encouraging more individuals to seek help and assessment without fear or embarrassment.
Furthermore, community-based initiatives that promote these early detection methods can empower individuals to take charge of their health. By facilitating access to resources and information, communities can support their members in achieving better cognitive health outcomes—ultimately creating a well-informed society that is more equipped to handle the challenges posed by neurodegenerative diseases.
Continued Research: Future Directions in Alzheimer’s Detection
The future of Alzheimer’s detection is ripe with potential, largely due to the growing body of research that highlights the effectiveness of olfactory tests. With the continued exploration of how these tests can be integrated into routine assessments, researchers are paving the way for groundbreaking advancements in early detection of the disease. Future studies may reveal even more nuanced associations between smell and cognitive function, enhancing our understanding of Alzheimer’s and its early indicators.
In the coming years, researchers aim to leverage technological advancements and broaden their studies to include diverse populations, accounting for variability in olfactory function across different cultures and languages. This inclusivity is critical as it not only validates the efficacy of these tests but also ensures that they are relevant and applicable to all individuals at risk of Alzheimer’s. As such, continued investment and innovation in this area of research hold promise for earlier and more effective Alzheimer’s interventions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Alzheimer’s early detection and why is it important?
Alzheimer’s early detection refers to identifying the first signs of cognitive impairment or memory loss associated with Alzheimer’s disease before significant symptoms develop. This is crucial because early diagnosis allows for timely interventions that can potentially slow the progression of the disease and improve quality of life.
How can olfactory tests be used for the early detection of Alzheimer’s disease?
Olfactory tests can help in the early detection of Alzheimer’s disease by assessing an individual’s ability to identify and remember smells. Research has shown that older adults with cognitive impairment often perform poorly on these tests, indicating a potential early warning sign for neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
What are the early signs of Alzheimer’s that can be detected?
Early signs of Alzheimer’s may include memory loss, difficulty in performing familiar tasks, language problems, and changes in mood or personality. Cognitive impairment tests, including olfactory tests, can help identify these signs to facilitate early intervention.
Are cognitive impairment tests reliable for Alzheimer’s diagnosis?
Cognitive impairment tests, especially those incorporating olfactory testing, have shown reliability in identifying individuals at risk for Alzheimer’s disease. These tests can detect subtle declines in cognition and memory, providing valuable insights into an individual’s risk.
What role does the home olfactory test play in Alzheimer’s early detection?
The home olfactory test plays a significant role in Alzheimer’s early detection by allowing individuals to perform assessments in the comfort of their homes. This non-invasive method can identify early signs of cognitive decline, making it easier for people to participate in monitoring their neurological health.
Can Alzheimer’s early detection lead to improved treatment outcomes?
Yes, Alzheimer’s early detection can lead to improved treatment outcomes. Identifying the disease in its initial stages allows for early interventions and the implementation of strategies to manage symptoms, potentially delaying the progression of Alzheimer’s and enhancing the quality of life.
What recent studies support the effectiveness of olfactory testing for Alzheimer’s?
Recent studies, including those conducted by researchers at Mass General Brigham, support the effectiveness of olfactory testing in detecting cognitive impairment related to Alzheimer’s disease. Participants with mild cognitive impairment scored lower on olfactory tests, indicating its potential as a tool for early detection.
How can understanding neurodegenerative diseases enhance Alzheimer’s early detection strategies?
Understanding neurodegenerative diseases enhances Alzheimer’s early detection strategies by providing insights into common warning signs and risk factors that can be monitored. This knowledge helps inform the development of tests, like olfactory assessments, that can identify at-risk individuals before significant symptoms arise.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Research Development | Olfactory tests created for at-home use to identify individuals at risk for Alzheimer’s. |
| Study Background | Conducted by researchers at Mass General Brigham, affiliated with Harvard University. |
| Test Methodology | Participants sniff odor labels, assessing their ability to discriminate, identify, and remember smells. |
| Target Population | Older adults, particularly those with cognitive impairment. |
| Findings | Participants with cognitive impairment scored lower on odor identification tests compared to cognitively normal individuals. |
| Implications | Could help identify individuals at risk of neurodegenerative diseases earlier. |
| Future Research | Further studies needed to track cognitive decline using olfactory testing. |
Summary
Alzheimer’s early detection is crucial for improving treatment outcomes, and recent research highlights a novel approach using olfactory testing. This study from Mass General Brigham shows that olfactory dysfunction can be an indicator of cognitive impairment, potentially allowing for safer, at-home assessments. Such innovations pave the way for identifying risks long before apparent symptoms arise, emphasizing the importance of proactive health measures in the management of Alzheimer’s disease.